Lipidomic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii reveals unusual polar lipids
- PMID: 17988103
- PMCID: PMC2576749
- DOI: 10.1021/bi7011993
Lipidomic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii reveals unusual polar lipids
Abstract
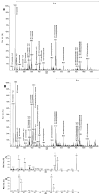
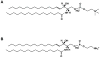
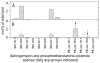
Analysis of the polar lipids of Toxoplasma gondii by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry provides a detailed picture of the lipid molecular species of this parasitic protozoan. Most notably, T. gondii contains a relatively high level, estimated to about 2% of the total polar lipid, of ceramide phosphoethanolamine. The ceramide phosphoethanolamine has a fatty amide profile with only 16- and 18-carbon species. Compared with the host fibroblasts in which it was grown, T. gondii also has higher levels of phosphatidylcholine but lower levels of sphingomyelin and phosphatidylserine. Analysis at the molecular species level indicated that T. gondii has greater amounts of shorter-chain fatty acid in its polar lipid molecular species than the host fibroblasts. Shorter-chain fatty acids with a combined total of 30 or fewer acyl carbons make up 21% of Toxoplasma's, but only 3% of the host's, diacyl phosphatidylcholine. Furthermore, diacyl phosphatidylcholine with two saturated acyl chains with 12, 14, or 16 carbons make up over 11% of parasite phosphatidylcholine but less than 3% of the host phosphatidylcholine molecular species. The distinctive T. gondii tachyzoite lipid profile may be particularly suited to the function of parasitic membranes and the interaction of the parasite with the host cell and the host's immune system. Combined with T. gondii genomic data, these lipidomic data will assist in elucidation of metabolic pathways for lipid biosynthesis in this important human pathogen.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lipids and fatty acids of tachyzoites and purified pellicles of Toxoplasma gondii.Parasitol Res. 1991;77(6):475-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00928412. Parasitol Res. 1991. PMID: 1924252
-
Lipidomic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites rhoptries: further insights into the role of cholesterol.Biochem J. 2008 Oct 1;415(1):87-96. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080795. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18564055
-
Toxoplasma acyl-CoA synthetase TgACS3 is crucial to channel host fatty acids in lipid droplets and for parasite propagation.J Lipid Res. 2024 Oct;65(10):100645. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100645. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 39306040 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of host lipids to Toxoplasma pathogenesis.Cell Microbiol. 2006 Jan;8(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00647.x. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16367861 Review.
-
Surface analysis of lipids by mass spectrometry: more than just imaging.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):329-53. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23623802 Review.
Cited by
-
Apicoplast-Localized Lysophosphatidic Acid Precursor Assembly Is Required for Bulk Phospholipid Synthesis in Toxoplasma gondii and Relies on an Algal/Plant-Like Glycerol 3-Phosphate Acyltransferase.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Aug 4;12(8):e1005765. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005765. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27490259 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylthreonine and Lipid-Mediated Control of Parasite Virulence.PLoS Biol. 2015 Nov 13;13(11):e1002288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002288. eCollection 2015. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 26565995 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis vs. salvage of ester- and ether-linked phosphatidylethanolamine in the intracellular protozoan pathogen Toxoplasma gondii.Commun Biol. 2023 Mar 22;6(1):306. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04664-x. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36949328 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the essential nature of Rab1B in Toxoplasma gondii.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Nov 8;16(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06030-6. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37941035 Free PMC article.
-
The flexibility of Apicomplexa parasites in lipid metabolism.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Mar 17;18(3):e1010313. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010313. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35298557 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McLeod R, Muench SP, Rafferty JB, Kyle DE, Mui EJ, Kirisits MJ, Mack DG, Roberts CW, Samuel BU, Lyons RE, Dorris M, Milhous WK, Rice DW. Triclosan inhibits the growth of Plasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii by inhibition of Apicomplexan Fab. I Int J Parasitol. 2001;31:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Roberts CW, McLeod R, Rice DW, Ginger M, Chance ML, Goad LJ. Fatty acid and sterol metabolism: potential antimicrobial targets in apicomplexan and trypanosomatic parasitic protozoa. Mol & Biochem Parasitol. 2003;126:129–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

