Identification and regulation of expression of a gene encoding a filamentous hemagglutinin-related protein in Bordetella holmesii
- PMID: 17988394
- PMCID: PMC2225982
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-100
Identification and regulation of expression of a gene encoding a filamentous hemagglutinin-related protein in Bordetella holmesii
Abstract
Background: Bordetella holmesii is a human pathogen closely related to B. pertussis, the etiological agent of whooping cough. It is able to cause disease in immunocompromised patients, but also whooping cough-like symptoms in otherwise healthy individuals. However, virtually nothing was known so far about the underlying virulence mechanisms and previous attempts to identify virulence factors related to those of B. pertussis were not successful.
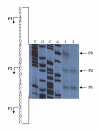
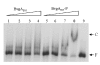
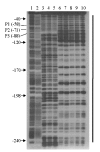
Results: By use of a PCR approach we were able to identify a B. holmesii gene encoding a protein with significant sequence similarities to the filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA) of B. avium and to a lesser extent to the FHA proteins of B. pertussis, B. parapertussis, and B. bronchiseptica. For these human and animal pathogens FHA is a crucial virulence factor required for successful colonization of the host. Interestingly, the B. holmesii protein shows a relatively high overall sequence similarity with the B. avium protein, while sequence conservation with the FHA proteins of the human and mammalian pathogens is quite limited and is most prominent in signal sequences required for their export to the cell surface. In the other Bordetellae expression of the fhaB gene encoding FHA was shown to be regulated by the master regulator of virulence, the BvgAS two-component system. Recently, we identified orthologs of BvgAS in B. holmesii, and here we show that this system also contributes to regulation of fhaB expression in B. holmesii. Accordingly, the purified BvgA response regulator of B. holmesii was shown to bind specifically in the upstream region of the fhaB promoter in vitro in a manner similar to that previously described for the BvgA protein of B. pertussis. Moreover, by deletion analysis of the fhaB promoter region we show that the BvgA binding sites are relevant for in vivo transcription from this promoter in B. holmesii.
Conclusion: The data reported here show that B. holmesii is endowed with a factor highly related to filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), a prominent virulence factor of the well characterized pathogenic Bordetellae. We show that like in the other Bordetellae the virulence regulatory BvgAS system is also involved in the regulation of fhaB expression in B. holmesii. Taken together these data indicate that in contrast to previous notions B. holmesii may in fact make use of virulence mechanisms related to those described for the other Bordetellae.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of the BvgAS two-component system of Bordetella holmesii.Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Nov;150(Pt 11):3715-3729. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27432-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15528658
-
Identification of BvgA-Dependent and BvgA-Independent Small RNAs (sRNAs) in Bordetella pertussis Using the Prokaryotic sRNA Prediction Toolkit ANNOgesic.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0004421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00044-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34550019 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple weak interactions between BvgA~P and ptx promoter DNA strongly activate transcription of pertussis toxin genes in Bordetella pertussis.PLoS Pathog. 2020 May 13;16(5):e1008500. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008500. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32401811 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction and virulence regulation in Bordetella pertussis.Microbiologia. 1996 Jun;12(2):185-96. Microbiologia. 1996. PMID: 8767703 Review.
-
The BvgS/BvgA phosphorelay system of pathogenic Bordetellae: structure, function and evolution.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:149-60. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792687 Review.
Cited by
-
Bordetella holmesii: Lipid A Structures and Corresponding Genomic Sequences Comparison in Three Clinical Isolates and the Reference Strain ATCC 51541.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 18;18(5):1080. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051080. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28524084 Free PMC article.
-
BipA Is Associated with Preventing Autoagglutination and Promoting Biofilm Formation in Bordetella holmesii.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 22;11(7):e0159999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159999. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27448237 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella holmesii: initial genomic analysis of an emerging opportunist.Pathog Dis. 2013 Mar;67(2):132-5. doi: 10.1111/2049-632X.12028. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Pathog Dis. 2013. PMID: 23620158 Free PMC article.
-
Resemblance and divergence: the "new" members of the genus Bordetella.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2010 Aug;199(3):155-63. doi: 10.1007/s00430-010-0148-z. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20390299 Review.
References
-
- Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, Holden MT, Churcher CM, Bentley SD, Mungall KL, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Temple L, James K, Harris B, Quail MA, Achtman M, Atkin R, Baker S, Basham D, Bason N, Cherevach L, Chillingworth T, Collins M, Cronin A, Davis P, Doggett J, Feltwell T, Goble A, Hamlin N, Hauser H, Holroyd S, Jagels K, Leather S, Moule S, Norberczak H, O'Neil S, Ormond D, Price C, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutter S, Sanders M, Saunders D, Seeger K, Sharp S, Simmonds M, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Unwin L, Whitehead S, Barrell BG, Maskell DJ. Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet. 2003;35:32–40. doi: 10.1038/ng1227. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

