Dual modes of Munc18-1/SNARE interactions are coupled by functionally critical binding to syntaxin-1 N terminus
- PMID: 17989281
- PMCID: PMC6673268
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3655-07.2007
Dual modes of Munc18-1/SNARE interactions are coupled by functionally critical binding to syntaxin-1 N terminus
Abstract
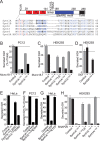
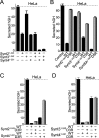
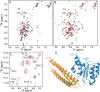
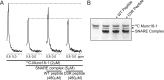
The SM (Sec1/Munc18-like) protein Munc18-1 and the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein (SNAP) receptor (SNARE) proteins syntaxin-1, SNAP-25, and synaptobrevin/VAMP (vesicle-associated membrane protein) constitute the core fusion machinery for synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Strikingly, Munc18-1 interacts with neuronal SNARE proteins in two distinct modes (i.e., with isolated syntaxin-1 alone in a "closed" conformation and with assembled SNARE complexes containing syntaxin-1 in an "open" conformation). However, it is unclear whether the two modes of Munc18/SNARE interactions are linked. We now show that both Munc18/SNARE interaction modes involve the same low-affinity binding of the extreme syntaxin-1 N terminus to Munc18-1, suggesting that this binding connects the two Munc18/SNARE interaction modes to each other. Using transfected cells as an in vitro assay system, we demonstrate that truncated syntaxins lacking a transmembrane region universally block exocytosis, but only if they contain a free intact N terminus. This block is enhanced by coexpression of either Munc18-1 or SNAP-25, suggesting that truncated syntaxins block exocytosis by forming an untethered inhibitory SNARE complex/Munc18-1 assembly in which the N-terminal syntaxin/Munc18 interaction is essential. Introduction of an N-terminal syntaxin peptide that disrupts this assembly blocks neurotransmitter release in the calyx of Held synapse, whereas a mutant peptide that does not disrupt the SNARE complex/Munc18 assembly has no effect. Viewed together, our data indicate that binding of Munc18 to the syntaxin N terminus unites different modes of Munc18/SNARE interactions and is essential for exocytic membrane fusion.
Figures



References
-
- Arac D, Murphy T, Rizo J. Facile detection of protein-protein interactions by one-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 2003;42:2774–2780. - PubMed
-
- Arac D, Dulubova I, Pei J, Huryeva I, Grishin NV, Rizo J. Three-dimensional structure of the rSly1 N-terminal domain reveals a conformational change induced by binding to syntaxin 5. J Mol Biol. 2005;346:589–601. - PubMed
-
- Bracher A, Weissenhorn W. Crystal structures of neuronal squid Sec1 implicate inter-domain hinge movement in the release of t-SNAREs. J Mol Biol. 2001;306:7–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
