Gene profiling of keloid fibroblasts shows altered expression in multiple fibrosis-associated pathways
- PMID: 17989729
- PMCID: PMC2933038
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701149
Gene profiling of keloid fibroblasts shows altered expression in multiple fibrosis-associated pathways
Abstract
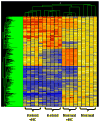
Keloids are benign tumors of the dermis that form during a protracted wound healing process. Susceptibility to keloid formation occurs predominantly in people of African and Asian descent. The key alteration(s) responsible for keloid formation has not been identified and there is no satisfactory treatment for this disorder. The altered regulatory mechanism is limited to dermal wound healing, although several diseases characterized by an exaggerated response to injury are prevalent in individuals of African ancestry. We have observed a complex pattern of phenotypic differences in keloid fibroblasts grown in standard culture medium or induced by hydrocortisone (HC). In this study Affymetrix-based microarray was performed on RNA obtained from fibroblasts cultured from normal scars and keloids grown in the absence and presence of HC. We observed differential regulation of approximately 500 genes of the 38,000 represented on the Affymetrix chip. Of particular interest was increased expression of several IGF-binding and IGF-binding-related proteins and decreased expression of a subset of Wnt pathway inhibitors and multiple IL-1-inducible genes. Increased expression of connective tissue growth factor and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 was observed in keloid fibroblasts only in the presence of HC. These findings support a role for multiple fibrosis-related pathways in the pathogenesis of keloids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilera O, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Herranz M, Espada J, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 (DKK-1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25:4116–4121. - PubMed
-
- August P, Suthanthiran M. Transforming growth factor beta and progression of renal disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003:S99–104. - PubMed
-
- Aune TM, Maas K, Moore JH, Olsen NJ. Gene expression profiles in human autoimmune disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:1905–1917. - PubMed
-
- Aune TM, Parker JS, Maas K, Liu Z, Olsen NJ, Moore JH. Co-localization of differentially expressed genes and shared susceptibility loci in human autoimmunity. Genet Epidemiol. 2004;27:162–172. - PubMed
-
- Barrett J. Keloid. In: Bergsma D, editor. Birth Defect Compendium. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkens Company; 1973. p. 553.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

