Persistence of DNA threads in human anaphase cells suggests late completion of sister chromatid decatenation
- PMID: 17989990
- PMCID: PMC2755729
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-007-0131-7
Persistence of DNA threads in human anaphase cells suggests late completion of sister chromatid decatenation
Abstract
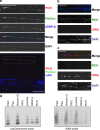
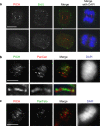
PICH (Plk1-interacting checkpoint helicase) was recently identified as an essential component of the spindle assembly checkpoint and shown to localize to kinetochores, inner centromeres, and thin threads connecting separating chromosomes even during anaphase. In this paper, we have used immuno-fiber fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromatin-immunoprecipitation to demonstrate that PICH associates with centromeric chromatin during anaphase. Furthermore, by careful analysis of PICH-positive anaphase threads through FISH as well as bromo-deoxyurdine and CREST labeling, we strengthen the evidence that these threads comprise mainly alphoid centromere deoxyribonucleic acid. Finally, by timing the addition of ICRF-193 (a specific inhibitor of topoisomerase-II alpha) to cells synchronized in anaphase, we demonstrate that topoisomerase activity is required specifically to resolve PICH-positive threads during anaphase (as opposed to being required to prevent the formation of such threads during earlier cell cycle stages). These data indicate that PICH associates with centromeres during anaphase and that most PICH-positive threads evolve from inner centromeres as these stretch in response to tension. Moreover, they show that topoisomerase activity is required during anaphase for the resolution of PICH-positive threads, implying that the complete separation of sister chromatids occurs later than previously assumed.
Figures


References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.tcb.2004.05.009', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2004.05.009'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15246429', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15246429/'}]}
- Amor DJ, Kalitsis P, Sumer H, Choo KH (2004) Building the centromere: from foundation proteins to 3D organization. Trends Cell Biol 14(7):359–368 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1456904', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1456904/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16547463', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16547463/'}]}
- Baird DM, Farr CJ (2006) The organization and function of chromosomes. EMBO Rep 7(4):372–376 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.041', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.041'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17218258', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17218258/'}]}
- Baumann C, Korner R, Hofmann K, Nigg EA (2007) PICH, a centromere-associated SNF2 family ATPase, is regulated by Plk1 and required for the spindle checkpoint. Cell 128(1):101–114 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80996-4', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80996-4'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8548831', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8548831/'}]}
- Bickmore WA, Oghene K (1996) Visualizing the spatial relationships between defined DNA sequences and the axial region of extracted metaphase chromosomes. Cell 84(1):95–104 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.gde.2007.02.009', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2007.02.009'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17320374', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17320374/'}]}
- Bloom K (2007) Centromere dynamics. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17(2):151–156 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

