Human serum albumin improves arterial dysfunction during early resuscitation in mouse endotoxic model via reduced oxidative and nitrosative stresses
- PMID: 17991713
- PMCID: PMC2111100
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070316
Human serum albumin improves arterial dysfunction during early resuscitation in mouse endotoxic model via reduced oxidative and nitrosative stresses
Abstract
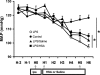
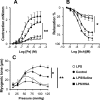
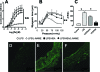
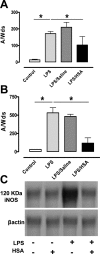
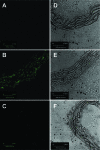
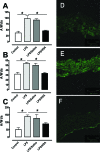
Human serum albumin (HSA) is used as a resuscitation fluid in sepsis. This study investigated the potential protective properties of HSA on vascular function in a mouse endotoxic model in terms of oxidative and nitrosative stresses. Swiss mice were treated with either lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (50 mg/kg i.p.) or vehicle. One and five hours later, mice were infused with HSA (4%, 10 ml/kg), normal saline (0.9% NaCl, 30 ml/kg), or no fluid. Six hours after treatment, vascular reactivity was assessed on aortae and small mesenteric arteries. Measurements of NO and superoxide anion (O2(-)) by spin trapping and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB, inducible NO synthase (iNOS), and peroxynitrite by Western blotting and immunohistochemical studies were conducted. HSA partially prevented the reduction of blood pressure induced by LPS and completely prevented both vascular hyporeactivity to phenylephrine and myogenic tone as well as endothelial dysfunction induced by the endotoxin. This was associated with a decreased up-regulation of NF-kappa B, iNOS, and peroxynitrite in the vascular wall. LPS-induced tissue increases in both NO and O2(-) production was decreased by HSA. These data demonstrate the protective effect of HSA treatment in experimental endotoxic shock by reducing the inflammatory process leading to oxidative and nitrosative stresses and vascular hyporeactivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated protein C improves lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiovascular dysfunction by decreasing tissular inflammation and oxidative stress.Crit Care Med. 2009 Jan;37(1):246-55. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318192fe4f. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19112282
-
Tetramethylpyradizine prevents inducible NO synthase expression and improves survival in rodent models of endotoxic shock.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999 Oct;360(4):435-44. doi: 10.1007/s002109900046. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10551281
-
Protection against endotoxic shock as a consequence of reduced nitrosative stress in MLCK210-null mice.Am J Pathol. 2007 Feb;170(2):439-46. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060219. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17255312 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of iNOS/sGC/PKG pathway, COX-2, CYP4A1, and gp91(phox) to the protective effect of 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, against vasodilation, hypotension, tachycardia, and inflammation in a rat model of septic shock.Nitric Oxide. 2013 Sep 1;33:18-41. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 14. Nitric Oxide. 2013. PMID: 23684565 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant human activated protein C improves endotoxemia-induced endothelial dysfunction: a blood-free model in isolated mouse arteries.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):H277-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01133.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19395546
Cited by
-
Association between Early Phase Serum Albumin Levels and Outcomes of Post-Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2022 Oct 29;12(11):1787. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111787. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36579497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between serum albumin to serum creatinine ratio and mortality risk in patients with heart failure.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Nov;16(11):2345-2355. doi: 10.1111/cts.13636. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37710402 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal management of hepatorenal syndrome in patients with cirrhosis.Hepat Med. 2010 Jun 21;2:87-98. doi: 10.2147/hmer.s6918. Hepat Med. 2010. PMID: 24367209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of serum biomarkers in predicting management strategies for acute pulmonary embolism.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 17;9(11):e21068. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21068. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027791 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of pregnancy, hypertension and nitric oxide inhibition on rat uterine artery myogenic reactivity.J Vasc Res. 2010;47(6):463-71. doi: 10.1159/000313874. Epub 2010 Apr 30. J Vasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20431295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parrillo JE. Pathogenetic mechanisms of septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1471–1477. - PubMed
-
- Russell JA. Management of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1699–1713. - PubMed
-
- Victor VM, Rocha M, De la Fuente M. Immune cells: free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004;4:327–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

