GRP78 and Cripto form a complex at the cell surface and collaborate to inhibit transforming growth factor beta signaling and enhance cell growth
- PMID: 17991893
- PMCID: PMC2223411
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01716-07
GRP78 and Cripto form a complex at the cell surface and collaborate to inhibit transforming growth factor beta signaling and enhance cell growth
Abstract
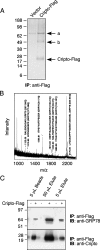
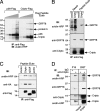
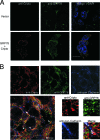
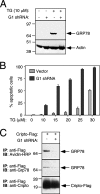
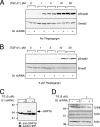
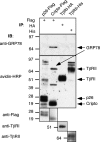
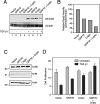
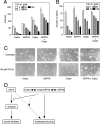
Cripto is a multifunctional cell surface protein with important roles in vertebrate embryogenesis and the progression of human tumors. While Cripto has been shown to modulate multiple signaling pathways, its binding partners do not appear to fully explain its molecular actions. Therefore, we conducted a screen aimed at identifying novel Cripto-interacting proteins. This screen led to our identification of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone that is also expressed at the surfaces of tumor cells. Here we demonstrate that Cripto and GRP78 interact at the cell surfaces of multiple cell lines and that their interaction is independent of prior association within the ER. Interestingly, short hairpin RNA knockdown of endogenous GRP78 resulted in enhanced transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling, indicating that like Cripto, GRP78 inhibits this pathway. We further show that when coexpressed, GRP78 and Cripto collaborate to antagonize TGF-beta responses, including Smad phosphorylation and growth inhibition of prostate cancer cells grown under anchorage-dependent or -independent conditions. Finally, we provide evidence that cells coexpressing GRP78 and Cripto grow much more rapidly in soft agar than do cells expressing either protein individually. Together, our results indicate that these proteins bind at the cell surface to enhance tumor growth via the inhibition of TGF-beta signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blockade of Cripto binding to cell surface GRP78 inhibits oncogenic Cripto signaling via MAPK/PI3K and Smad2/3 pathways.Oncogene. 2009 Jun 18;28(24):2324-36. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.97. Epub 2009 May 4. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19421146 Free PMC article.
-
Cripto binds transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and inhibits TGF-beta signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9268-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01168-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030617 Free PMC article.
-
Cripto haploinsufficiency affects in vivo colon tumor development.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jul;45(1):31-40. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2412. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24805056 Free PMC article.
-
Cripto/GRP78 modulation of the TGF-β pathway in development and oncogenesis.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 4;586(14):1836-45. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.01.051. Epub 2012 Feb 1. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22306319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted role of the embryonic gene Cripto-1 in cancer, stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Dec;29:51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 25153355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GRP78 Protein Expression as Prognostic Values in Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy and Laparoscopic Surgery for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer.Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;47(4):804-12. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.121. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25687871 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interleukin 34 (IL-34) cell-surface localization regulated by the molecular chaperone 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein facilitates the differentiation of monocytic cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2386-2396. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006226. Epub 2018 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30573681 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibody against cell surface GRP78 as a novel agent in suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling, tumor growth, and metastasis.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Dec 15;19(24):6802-11. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1106. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24048331 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of phosphorylation-dependent binding partners of aquaporin-2 using protein mass spectrometry.J Proteome Res. 2009 Mar;8(3):1540-54. doi: 10.1021/pr800894p. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19209902 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Surface GRP78 as a Death Receptor and an Anticancer Drug Target.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 13;11(11):1787. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111787. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31766302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adkins, H. B., C. Bianco, S. G. Schiffer, P. Rayhorn, M. Zafari, A. E. Cheung, O. Orozco, D. Olson, A. De Luca, L. L. Chen, K. Miatkowski, C. Benjamin, N. Normanno, K. P. Williams, M. Jarpe, D. LePage, D. Salomon, and M. Sanicola. 2003. Antibody blockade of the Cripto CFC domain suppresses tumor cell growth in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 112575-587. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arap, M. A., J. Lahdenranta, P. J. Mintz, A. Hajitou, A. S. Sarkis, W. Arap, and R. Pasqualini. 2004. Cell surface expression of the stress response chaperone GRP78 enables tumor targeting by circulating ligands. Cancer Cell 6275-284. - PubMed
-
- Bernales, S., F. R. Papa, and P. Walter. 2006. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22487-508. - PubMed
-
- Bianco, C., S. Kannan, M. De Santis, M. Seno, C. K. Tang, I. Martinez-Lacaci, N. Kim, B. Wallace-Jones, M. E. Lippman, A. D. Ebert, C. Wechselberger, and D. S. Salomon. 1999. Cripto-1 indirectly stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of erb B-4 through a novel receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2748624-8629. - PubMed
-
- Bianco, C., L. Strizzi, A. Rehman, N. Normanno, C. Wechselberger, Y. Sun, N. Khan, M. Hirota, H. Adkins, K. Williams, R. U. Margolis, M. Sanicola, and D. S. Salomon. 2003. A Nodal- and ALK4-independent signaling pathway activated by Cripto-1 through glypican-1 and c-Src. Cancer Res. 631192-1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
