The parathyroid is a target organ for FGF23 in rats
- PMID: 17992255
- PMCID: PMC2066196
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI32409
The parathyroid is a target organ for FGF23 in rats
Abstract
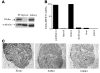
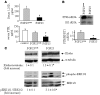
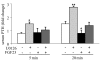
Phosphate homeostasis is maintained by a counterbalance between efflux from the kidney and influx from intestine and bone. FGF23 is a bone-derived phosphaturic hormone that acts on the kidney to increase phosphate excretion and suppress biosynthesis of vitamin D. FGF23 signals with highest efficacy through several FGF receptors (FGFRs) bound by the transmembrane protein Klotho as a coreceptor. Since most tissues express FGFR, expression of Klotho determines FGF23 target organs. Here we identify the parathyroid as a target organ for FGF23 in rats. We show that the parathyroid gland expressed Klotho and 2 FGFRs. The administration of recombinant FGF23 led to an increase in parathyroid Klotho levels. In addition, FGF23 activated the MAPK pathway in the parathyroid through ERK1/2 phosphorylation and increased early growth response 1 mRNA levels. Using both rats and in vitro rat parathyroid cultures, we show that FGF23 suppressed both parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion and PTH gene expression. The FGF23-induced decrease in PTH secretion was prevented by a MAPK inhibitor. These data indicate that FGF23 acts directly on the parathyroid through the MAPK pathway to decrease serum PTH. This bone-parathyroid endocrine axis adds a new dimension to the understanding of mineral homeostasis.
Figures
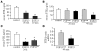
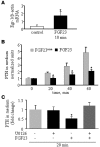
References
-
- Liu S., et al. Pathogenic role of Fgf23 in Hyp mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006;291:E38–E49. - PubMed
-
- Kolek O.I., et al. 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 upregulates FGF23 gene expression in bone: the final link in a renal-gastrointestinal-skeletal axis that controls phosphate transport. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G1036–G1042. - PubMed
-
- Liu S., et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is a counter-regulatory phosphaturic hormone for vitamin D. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006;17:1305–1315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

