Identification of the bchP gene, encoding geranylgeranyl reductase in Chlorobaculum tepidum
- PMID: 17993528
- PMCID: PMC2223686
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01430-07
Identification of the bchP gene, encoding geranylgeranyl reductase in Chlorobaculum tepidum
Abstract
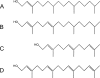
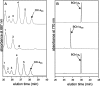
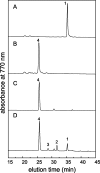
The Chlorobaculum tepidum genome contains two paralogous genes, CT2256 and CT1232, whose products are members of the FixC dehydrogenase superfamily and have sequence similarity to geranylgeranyl reductases. Each gene was insertionally inactivated, and the resulting mutants were characterized. CT2256 encodes geranylgeranyl reductase (BchP); CT1232 is not involved in bacteriochlorophyll or chlorophyll biosynthesis.
Figures
References
-
- Addlesee, H. A., L. C. D. Gibson, P. E. Jensen, and C. N. Hunter. 1996. Cloning, sequencing and functional assignment of the chlorophyll biosynthesis gene, chlP, of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. FEBS Lett. 389126-130. - PubMed
-
- Beale, S. I. 1999. Enzymes of chlorophyll biosynthesis. Photosynth. Res. 6043-73.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

