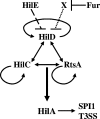
Fur regulates expression of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system through HilD
- PMID: 17993530
- PMCID: PMC2223717
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00926-07
Fur regulates expression of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system through HilD
Abstract
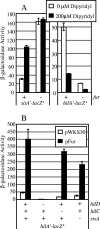
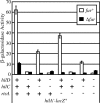
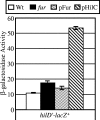
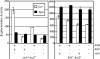
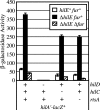
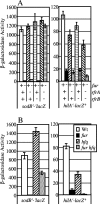
The invasion of intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is mediated by a type III secretion system (T3SS) encoded on Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1). Expression of the SPI1 T3SS is tightly regulated by the combined action of HilC, HilD, and RtsA, three AraC family members that can independently activate hilA, which encodes the direct regulator of the SPI1 structural genes. Expression of hilC, hilD, and rtsA is controlled by a number of regulators that respond to a variety of environmental signals. In this work, we show that one such signal is iron mediated by Fur (ferric uptake regulator). Fur activates hilA transcription in a HilD-dependent manner. Fur regulation of HilD does not appear to be simply at the transcriptional or translational level but rather requires the presence of the HilD protein. Fur activation of SPI1 is not mediated through the Fur-regulated small RNAs RfrA and RfrB, which are the Salmonella ortholog and paralog of RyhB that control expression of sodB. Fur regulation of HilD is also not mediated through the known SPI1 repressor HilE or the CsrABC system. Although understanding the direct mechanism of Fur action on HilD requires further analysis, this work is an important step toward elucidating how various global regulatory systems control SPI1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HilD, HilC and RtsA constitute a feed forward loop that controls expression of the SPI1 type three secretion system regulator hilA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Aug;57(3):691-705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04737.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16045614
-
HilD, HilC, and RtsA Form Homodimers and Heterodimers To Regulate Expression of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island I Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2020 Apr 9;202(9):e00012-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-20. Print 2020 Apr 9. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32041797 Free PMC article.
-
HilE Regulates HilD by Blocking DNA Binding in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00750-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00750-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378886 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
-
Salmonella invasion gene regulation: a story of environmental awareness.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:110-7. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765064 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between virulence loci: regulation of Salmonella enterica pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) by products of the std fimbrial operon.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030499. Epub 2012 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22291968 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella invasion is controlled through the secondary structure of the hilD transcript.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Apr 24;15(4):e1007700. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007700. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31017982 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction pathway mediated by the novel regulator LoiA for low oxygen tension induced Salmonella Typhimurium invasion.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 2;13(6):e1006429. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006429. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28575106 Free PMC article.
-
The battle for iron in enteric infections.Immunology. 2020 Nov;161(3):186-199. doi: 10.1111/imm.13236. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 32639029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of the Resistance Responses to Stress Conditions Encountered in Food and Food Processing Environments on the Virulence and Growth Fitness of Non-Typhoidal Salmonellae.Foods. 2021 Mar 14;10(3):617. doi: 10.3390/foods10030617. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33799446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmer, B. M., J. van Reeuwijk, P. R. Watson, T. S. Wallis, and F. Heffron. 1999. Salmonella SirA is a global regulator of genes mediating enteropathogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 31971-982. - PubMed
-
- Altier, C., M. Suyemoto, A. I. Ruiz, K. D. Burnham, and R. Maurer. 2000. Characterization of two novel regulatory genes affecting Salmonella invasion gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 35635-646. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1995. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol. Microbiol. 18715-727. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22703-714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

