Autoantibodies to the C-terminal subunit of RLIP76 induce oxidative stress and endothelial cell apoptosis in immune-mediated vascular diseases and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 17993611
- PMCID: PMC2343593
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-092825
Autoantibodies to the C-terminal subunit of RLIP76 induce oxidative stress and endothelial cell apoptosis in immune-mediated vascular diseases and atherosclerosis
Abstract
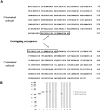
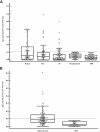
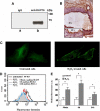
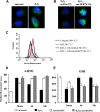
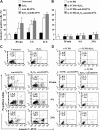
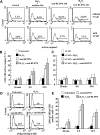
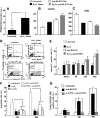
Although detection of autoantibodies in the peripheral blood from patients with immune-mediated endothelial dysfunctions has so far failed to provide tools of diagnostic or pathogenetic value, putative bioindicators include anti-endothelial cell antibodies, a heterogeneous family of antibodies that react with autoantigens expressed by endothelial cells. In this study, to identify endothelial autoantigens involved in the autoimmune processes causing endothelial damage, we screened a human microvascular endothelial cell cDNA library with sera from patients with Behçet's disease. We identified antibodies to the C-terminus of Ral binding protein1 (RLIP76), a protein that catalyzes the ATP-dependent transport of glutathione (GSH) conjugates including GSH-4-hydroxy-t-2,3-nonenal, in the serum of a significant percentage of patients with various diseases characterized by immune-mediated endothelial dysfunction, including Behçet disease, systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus and carotid atherosclerosis. These autoantibodies increased intracellular levels of 4-hydroxy-t-2,3-nonenal, decreased levels of GSH and activated C-Jun NH2 Kinase signaling (JNK), thus inducing oxidative stress-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. The dietary antioxidant alpha-tocopherol counteracted endothelial cell demise. These findings suggest that autoantibodies to RLIP76 play a pathogenetic role in immune-mediated vascular diseases and represent a valuable peripheral blood bioindicator of atherosclerosis and immune-mediated vascular diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Lee SJ, Kavanaugh A. 4. Autoimmunity, vasculitis, and autoantibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:S445–S450. - PubMed
-
- Martin F, Chan AC. Pathogenic roles of B cells in human autoimmunity; insights from the clinic. Immunity. 2004;20:517–527. - PubMed
-
- Meroni P, Ronda N, Raschi E, Borghi MO. Humoral autoimmunity against endothelium: theory or reality? Trends Immunol. 2005;26:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Youinou P, Le Dantec C, Bendaoud B, Renaudineau Y, Pers JO, Jamin C. Endothelium, a target for immune-mediated assault in connective tissue disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2006;5:222–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

