Relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons for apoptosis in mouse hair follicles
- PMID: 17993746
- PMCID: PMC2868148
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.4.335
Relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons for apoptosis in mouse hair follicles
Abstract
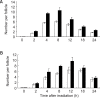
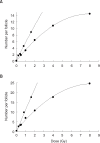
This study compared the effects of high linear energy transfer (LET) fast neutrons on the induction of apoptosis in the hair follicles of ICR mice with those of low LET (60)Co gamma-rays. The changes that occurred from 0 to 24 h after exposing the mice to either 2 Gy of gamma-rays (2 Gy/min) or 0.8 Gy of neutrons (94 mGy/min, 35 MeV) were examined. The maximum frequency was found at 12 h (gamma-rays) or 8 h (neutrons) after irradiation. The mice that received 0-8 Gy of gamma-rays or 0-1.6 Gy of neutrons were examined 8 h after irradiation. The dose-response curves were analyzed using the best-fit curve model. The dose-response curves were linear-quadratic, and a significant relationship was found between the frequency of apoptotic cells and the dose. The morphological findings in the irradiated groups were typical apoptotic fragments in the matrix region of the hair follicle, but the spontaneous existence of apoptotic fragments was rarely observed in the control group. In the presence of an apoptosis frequency between 2 and 14 per follicle, the relative biological effectiveness values of neutrons in small and large follicles were 2.09 +/- 0.30 and 2.15 +/- 0.18, respectively.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons in a multiorgan assay for apoptosis in mouse.Environ Toxicol. 2008 Apr;23(2):233-9. doi: 10.1002/tox.20328. Environ Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18214905
-
Measurement of apoptotic fragments in growing hair follicles following gamma-ray irradiation in mice.Anticancer Res. 1996 Jan-Feb;16(1):189-92. Anticancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8615607
-
Apoptosis induced by fast neutrons versus 60Co gamma-rays in human peripheral blood lymphocytes.Int J Radiat Biol. 1998 Mar;73(3):289-95. doi: 10.1080/095530098142383. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998. PMID: 9525257
-
Tissue responses to low protracted doses of high LET radiations or photons: early and late damage relevant to radio-protective countermeasures.Adv Space Res. 1989;9(10):299-313. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(89)90453-5. Adv Space Res. 1989. PMID: 11537307 Review.
-
Effects of gamma rays on the regeneration of murine hair follicles in the natural hair cycle.Int J Radiat Biol. 2017 Sep;93(9):937-946. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2017.1344362. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Int J Radiat Biol. 2017. PMID: 28627318 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Medical Uses and Cellular Effects of High and Low Linear Energy Transfer Radiation.Toxics. 2022 Oct 21;10(10):628. doi: 10.3390/toxics10100628. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36287908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blöcher D. DNA double-strand break repair determines the RBE of α-particles. Int J Radiat Biol. 1988;54:761–771. - PubMed
-
- Britten RA, Peters LJ, Murray D. Biological factors influencing the RBE of neutrons: implications for their past, present and future use in radiotherapy. Radiat Res. 2001;156:125–135. - PubMed
-
- Broerse JJ, Barendsen GW. Relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons for effects on normal Tissues. Curr Top Radiat Res Q. 1973;8:305–350. - PubMed
-
- Denekamp J, Joiner MC, Maughan RL. Neutron RBEs for mouse skin at low doses per fraction. Radiat Res. 1984;98:317–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

