Phytotherapeutic effects of Echinacea purpurea in gamma-irradiated mice
- PMID: 17993747
- PMCID: PMC2868149
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.4.341
Phytotherapeutic effects of Echinacea purpurea in gamma-irradiated mice
Abstract
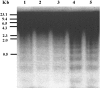
Echinacea (E.) purpurea herb is commonly known as the purple coneflower, red sunflower and rudbeckia. In this paper, we report the curative efficacy of an Echinacea extract in gamma-irradiated mice. E. purpurea was given to male mice that were divided into five groups (control, treated, irradiated, treated before irradiation & treated after irradiation) at a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight for 2 weeks before and after irradiation with 3 Gy of gamma-rays. The results reflected the detrimental reduction effects of gamma-rays on peripheral blood hemoglobin and the levels of red blood cells, differential white blood cells, and bone marrow cells. The thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARs) level, Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSPx) activities and DNA fragmentation were also investigated. FT-Raman spectroscopy was used to explore the structural changes in liver tissues. Significant changes were observed in the microenvironment of the major constituents, including tyrosine and protein secondary structures. E. purpurea administration significantly ameliorated all estimated parameters. The radio-protection effectiveness was similar to the radio-recovery curativeness in comparison to the control group in most of the tested parameters. The radio-protection efficiency was greater than the radio-recovery in hemoglobin level during the first two weeks, in lymphoid cell count and TBARs level at the fourth week and in SOD activity during the first two weeks, as compared to the levels of these parameters in the control group.
Figures
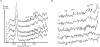
Similar articles
-
Curcumin protection activities against γ-rays-induced molecular and biochemical lesions.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Sep 21;6:375. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-375. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 24053347 Free PMC article.
-
Radioprotective effects of Aloe vera leaf extract on Swiss albino mice against whole-body gamma irradiation.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2009;28(1):53-61. doi: 10.1615/jenvironpatholtoxicoloncol.v28.i1.60. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19392655
-
Studies on the protective effects of Boerhaavia diffusa L. against gamma radiation induced damage in mice.Integr Cancer Ther. 2007 Dec;6(4):381-8. doi: 10.1177/1534735407309743. Integr Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 18048886
-
Protection from lethal and sub-lethal whole body exposures of mice to γ-radiation by Acorus calamus L.: studies on tissue antioxidant status and cellular DNA damage.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012 Jan;64(1-2):57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2010.06.006. Epub 2010 Jul 5. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 20605086
-
Applications of the phytomedicine Echinacea purpurea (Purple Coneflower) in infectious diseases.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:769896. doi: 10.1155/2012/769896. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22131823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin protection activities against γ-rays-induced molecular and biochemical lesions.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Sep 21;6:375. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-375. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 24053347 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo studies of the immunomodulatory effect of Echinacea purpurea on dendritic cells.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2015 Dec;13(2):185-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 30647582 Free PMC article.
-
Can Echinacea be a potential candidate to target immunity, inflammation, and infection - The trinity of coronavirus disease 2019.Heliyon. 2021 Feb;7(2):e05990. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e05990. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33585706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of murine exposure to gamma rays on the interplay between Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Apr 9;6:74. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00074. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25914644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou-Elella AMKE, Siendones E, Padillo J, Montero JL, De la Mata M, Muntané Relat J. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and nitric oxide mediate apoptosis by D-galactosamine in a primary culture of rat hepatocytes: exacerbation of cell death by cocultured Kupffer cells. Can J Gastroenterol. 2002;16:791–799. - PubMed
-
- Ang-Lee MK, Moss J, Yuan CS. Herbal medicines and perioperative care. JAMA. 2001;286:208–216. - PubMed
-
- Barrett B. Medicinal properties of Echinacea: a critical review. Phytomedicine. 2003;10:66–86. - PubMed
-
- Barrett B. Echinacea: a safety review. HerbalGram. 2003;57:36–39.
-
- Bauer R. New knowledge regarding the effect and effectiveness of Echinacea purpurea extracts. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2002;152:407–411. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

