Rapid control of protein level in the apicomplexan Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 17994029
- PMCID: PMC2601725
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth1134
Rapid control of protein level in the apicomplexan Toxoplasma gondii
Erratum in
- Nat Methods. 2008 Jan;5(1):113
Abstract
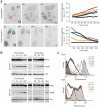
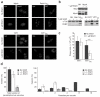
Analysis of gene function in apicomplexan parasites is limited by the absence of reverse genetic tools that allow easy and rapid modulation of protein levels. The fusion of a ligand-controlled destabilization domain (ddFKBP) to a protein of interest enables rapid and reversible protein stabilization in T. gondii. This allows an efficient functional analysis of proteins that have a dual role during host cell invasion and/or intracellular growth of the parasite.
Figures
Comment in
-
Switching parasite proteins on and off.Nat Methods. 2007 Dec;4(12):999-1000. doi: 10.1038/nmeth1207-999. Nat Methods. 2007. PMID: 18049467 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

