An evaluation of levalbuterol HFA in the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm
- PMID: 17994402
- PMCID: PMC2409177
- DOI: 10.1080/02770900701595667
An evaluation of levalbuterol HFA in the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm
Abstract
Background: Exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB) affects up to 90% of all patients with asthma. Objective. This study evaluated the ability of levalbuterol hydrofluoroalkane (HFA) 90 mug (two actuations of 45 microg) administered via metered dose inhaler (MDI) to protect against EIB in mild-to-moderate asthmatics.
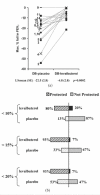
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-way cross-over study. Patients with asthma (n = 15) were > or =18 years, had a > or =6-month history of EIB, > or = 70% baseline predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), and a 20% to 50% decrease in FEV(1) after treadmill exercise challenge using single-blind placebo MDI. Levalbuterol or placebo was self-administered 30 minutes before exercise. Treatment sequences were separated by a 3-to 7-day washout period. Spirometry was performed predose, 20 minutes postdose/pre-exercise, and 5, 10, 15, 30, and 60 minutes post-exercise. The primary endpoint was the maximum percent decrease in FEV1 from baseline (postdose/pre-exercise). The percentage of protected (< or = 20% decrease in post-exercise FEV1) patients was also assessed.
Results: Levalbuterol had significantly smaller maximum percent post-exercise decrease in FEV1 compared with placebo (LS mean +/- SE; -4.8% +/- 2.8% versus -22.5% +/- 2.8%, respectively). For levalbuterol, 14/15 (93.3%) patients had < 20% decrease in post-exercise FEV1 compared with 8/15 (53.3%) for placebo (p = 0.0143). Treatment was well tolerated.
Conclusion: Levalbuterol HFA MDI (90 microg) administered 30 minutes before exercise was significantly more effective than placebo in protecting against EIB after a single exercise challenge and was well tolerated.
Clinical implications: Levalbuterol HFA MDI when administered before exercise was effective in protecting adults with asthma from EIB.
Figures

References
-
- Parsons JP, Mastronarde JG. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in athletes. Chest. 2005;128:3966–3974. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SD, Caillaud C, Brannan JD. Beta2-agonists and exercise-induced asthma. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2006;31:163–180. - PubMed
-
- Clark CJ, Cochrane LM. Physical activity and asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1999;5:68–75. - PubMed
-
- Meyer R, Kroner-Herwig B, Sporkel H. The effect of exercise and induced expectations on visceral perception in asthmatic patients. J Psychosom Res. 1990;34:455–460. - PubMed
-
- Ergood JS, Epstein LH, Ackerman M, Fireman P. Perception of expiratory flow by asthmatics and non-asthmatics during rest and exercise. Health Psychol. 1985;4:545–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
