Label-free molecular imaging of atherosclerotic lesions using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy
- PMID: 17994895
- PMCID: PMC2646612
- DOI: 10.1117/1.2795437
Label-free molecular imaging of atherosclerotic lesions using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy
Abstract
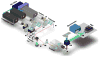
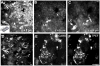
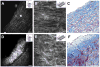
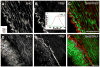
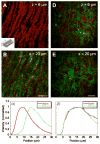
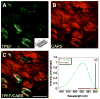
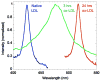
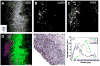
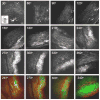
Arterial tissues collected from Ossabaw swine bearing metabolic syndrome-induced cardiovascular plaques are characterized by multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy that allows coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering, second-harmonic generation, and two-photon excitation fluorescence imaging on the same platform. Significant components of arterial walls and atherosclerotic lesions, including endothelial cells, extracellular lipid droplets, lipid-rich cells, low-density lipoprotein aggregates, collagen, and elastin are imaged without any labeling. Emission spectra of these components are obtained by nonlinear optical microspectrometry. The nonlinear optical contrast is compared with histology of the same sample. Multimodal nonlinear optical imaging of plaque composition also allows identification of atherosclerotic regions that are vulnerable to rupture risk. The demonstrated capability of nonlinear optical microscopy for label-free molecular imaging of atherosclerotic lesions with 3-D submicrometric resolution suggests its potential application to the diagnosis of atherosclerotic plaques, determination of their rupture risk, and design of individualized drug therapy based on plaque composition.
Figures

References
-
- Rosamond W, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2007 update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115:69–e171. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature (London) 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Fayad ZA, Fuster V. Clinical imaging of the high-risk or vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque. Circ Res. 2001;89:305–316. - PubMed
-
- Fischer A, Gutstein DE, Fayad ZA, Fuster V. Predicting plaque rupture: enhancing diagnosis and clinical decision-making in coronary artery disease. Vasc Med. 2000;5:163–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

