Carnosic acid, a catechol-type electrophilic compound, protects neurons both in vitro and in vivo through activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway via S-alkylation of targeted cysteines on Keap1
- PMID: 17995931
- PMCID: PMC4566957
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05039.x
Carnosic acid, a catechol-type electrophilic compound, protects neurons both in vitro and in vivo through activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway via S-alkylation of targeted cysteines on Keap1
Abstract
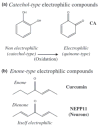
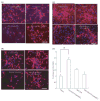
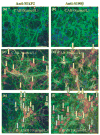
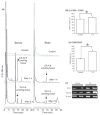
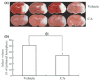
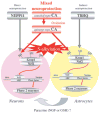
Electrophilic compounds are a newly recognized class of redox-active neuroprotective compounds with electron deficient, electrophilic carbon centers that react with specific cysteine residues on targeted proteins via thiol (S-)alkylation. Although plants produce a variety of physiologically active electrophilic compounds, the detailed mechanism of action of these compounds remains unknown. Catechol ring-containing compounds have attracted attention because they become electrophilic quinones upon oxidation, although they are not themselves electrophilic. In this study, we focused on the neuroprotective effects of one such compound, carnosic acid (CA), found in the herb rosemary obtained from Rosmarinus officinalis. We found that CA activates the Keap1/Nrf2 transcriptional pathway by binding to specific Keap1 cysteine residues, thus protecting neurons from oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. In cerebrocortical cultures, CA-biotin accumulates in non-neuronal cells at low concentrations and in neurons at higher concentrations. We present evidence that both the neuronal and non-neuronal distribution of CA may contribute to its neuroprotective effect. Furthermore, CA translocates into the brain, increases the level of reduced glutathione in vivo, and protects the brain against middle cerebral artery ischemia/reperfusion, suggesting that CA may represent a new type of neuroprotective electrophilic compound.
Figures
References
-
- Ahlgren-Beckendorf JA, Reising AM, Schander MA, Herdler JW, Johnson JA. Coordinate regulation of NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase and glutathione-S-transferase in primary cultures of rat neurons and glias: role of the antioxidant/electrophile responsive element. Glia. 1999;15:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally S, Choi AM, Cook JL. Nrf2, a cap’n’collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26071–26078. - PubMed
-
- Ankacrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P. Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron. 1995;15:961–973. - PubMed
-
- Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Aeschbach R, Loligers J. Antioxidant and pro oxidant properties of active rosemary constituents: carnosol and carnosic acid. Xenobiotica. 1992;22:257–268. - PubMed
-
- Barco A, Bailey CH, Kandel ER. Common molecular mechanisms in explicit and implicit memory. J Neurochem. 2006;97:1520–1533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

