PACAP-38 induces neuronal differentiation of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via cAMP-mediated activation of ERK and p38 MAP kinases
- PMID: 17995938
- PMCID: PMC2230095
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05018.x
PACAP-38 induces neuronal differentiation of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via cAMP-mediated activation of ERK and p38 MAP kinases
Abstract
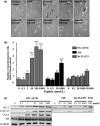
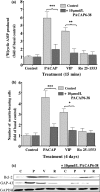
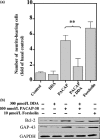
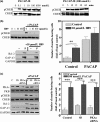
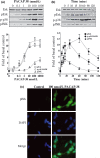
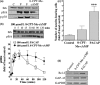
The intracellular signaling pathways mediating the neurotrophic actions of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) were investigated in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Previously, we showed that SH-SY5Y cells express the PAC(1) and VIP/PACAP receptor type 2 (VPAC(2)) receptors, and that the robust cAMP production in response to PACAP and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) was mediated by PAC(1) receptors (Lutz et al. 2006). Here, we investigated the ability of PACAP-38 to differentiate SH-SY5Y cells by measuring morphological changes and the expression of neuronal markers. PACAP-38 caused a concentration-dependent increase in the number of neurite-bearing cells and an up-regulation in the expression of the neuronal proteins Bcl-2, growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and choline acetyltransferase: VIP was less effective than PACAP-38 and the VPAC(2) receptor-specific agonist, Ro 25-1553, had no effect. The effects of PACAP-38 and VIP were blocked by the PAC(1) receptor antagonist, PACAP6-38. As observed with PACAP-38, the adenylyl cyclase activator, forskolin, also induced an increase in the number of neurite-bearing cells and an up-regulation in the expression of Bcl-2 and GAP-43. PACAP-induced differentiation was prevented by the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor, 2',5'-dideoxyadenosine (DDA), but not the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor, H89, or by siRNA-mediated knock-down of the PKA catalytic subunit. PACAP-38 and forskolin stimulated the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP; p38 MAP kinase) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). PACAP-induced neuritogenesis was blocked by the MEK1 inhibitor PD98059 and partially by the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor SB203580. Activation of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac) partially mimicked the effects of PACAP-38, and led to the phosphorylation of ERK but not p38 MAP kinase. These results provide evidence that the neurotrophic effects of PACAP-38 on human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells are mediated by the PAC(1) receptor through a cAMP-dependent but PKA-independent mechanism, and furthermore suggest that this involves Epac-dependent activation of ERK as well as activation of the p38 MAP kinase signaling pathway.
Figures
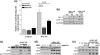
Similar articles
-
Neurotrophic actions of PACAP-38 and LIF on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.J Mol Neurosci. 2008 Nov;36(1-3):45-56. doi: 10.1007/s12031-008-9082-6. Epub 2008 May 28. J Mol Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18506635
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in injured spinal cord and in activated microglia via a cAMP-dependent pathway.J Neurosci. 2000 May 15;20(10):3622-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-10-03622.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10804204 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of peptide histidine isoleucine (PHI) and related peptides on stimulation and suppression of neuroblastoma cell proliferation. A novel VIP-independent action of PHI via MAP kinase.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 31;273(31):19685-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.31.19685. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9677397
-
Regulation of PC12 cell differentiation by cAMP signaling to ERK independent of PKA: do all the connections add up?Sci STKE. 2007 Apr 17;2007(382):pe15. doi: 10.1126/stke.3822007pe15. Sci STKE. 2007. PMID: 17440132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide receptors as cancer drug targets.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Nov;1455(1):141-148. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14100. Epub 2019 May 10. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 31074514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the VPAC2 Receptor Impairs Axon Outgrowth and Decreases Dendritic Arborization in Mouse Cortical Neurons by a PKA-Dependent Mechanism.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 4;14:521. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00521. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32581681 Free PMC article.
-
PACAP enhances axon outgrowth in cultured hippocampal neurons to a comparable extent as BDNF.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 25;10(3):e0120526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120526. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25807538 Free PMC article.
-
EPAC proteins transduce diverse cellular actions of cAMP.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;158(1):70-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00087.x. Epub 2009 Feb 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19210747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epac and PKA: a tale of two intracellular cAMP receptors.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008 Jul;40(7):651-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00438.x. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008. PMID: 18604457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential responses of Trans-Resveratrol on proliferation of neural progenitor cells and aged rat hippocampal neurogenesis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 23;6:28142. doi: 10.1038/srep28142. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27334554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alleaume C, Eychène A, Harnois T, Bourmeyster N, Constantin B, Caigneaux E, Muller J-M, Philippe M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide-induced neurite remodeling in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells implicates the cdc42 GTPase and is independent of Ras-ERK pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2004;299:511–524. - PubMed
-
- Boeshore KL, Schreiber RC, Vaccariello SA, Sachs HH, Salazar R, Lee J, Ratan RR, Leahy P, Zigmond RE. Novel changes in gene expression following axotomy of a sympathetic ganglion: a microarray analysis. J. Neurobiol. 2004;59:216–235. - PubMed
-
- Borba JC, Henze IP, Silveira MS, Kubrusly RC, Gardino PF, de Mello MC, Hokoc JN, de Mello FG. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) can act as determinant of the tyrosine hydroxylase phenotype of dopaminergic cells during retina development. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2005;156:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau RTM, Hoskin DW, Lin T-J. Phosphatase inhibition potentiates IL-6 production by mast cells in response to FcεRI-mediated activation: involvement of p38 MAPK. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004;76:1075–1081. - PubMed
-
- Braas KM, May V. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptides, PACAP-38 and PACAP-27, regulation of sympathetic neuron catecholamine, and neuropeptide Y expression through activation of type I PACAP/VIP receptor isoforms. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1996;805:204–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

