Altered expression and subcellular distribution of GRK subtypes in the dopamine-depleted rat basal ganglia is not normalized by l-DOPA treatment
- PMID: 17996024
- PMCID: PMC2628845
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05104.x
Altered expression and subcellular distribution of GRK subtypes in the dopamine-depleted rat basal ganglia is not normalized by l-DOPA treatment
Abstract
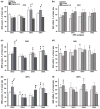
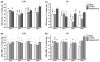
Dysregulation of dopamine (DA) receptors is believed to underlie Parkinson's disease pathology and l-DOPA-induced motor complications. DA receptors are subject to regulation by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) and arrestins. DA lesion with 6-hydroxydopamine caused multiple protein- and brain region-specific changes in the expression of GRKs. In the globus pallidus, all four GRK isoforms (GRK2, 3, 5, 6) were reduced in the lesioned hemisphere. In the caudal caudate-putamen (cCPu) three GRK isoforms (GRK2, 3, 6) were decreased by DA depletion. The decrease in GRK proteins in globus pallidus, but not cCPu, was mirrored by reduction in mRNA. GRK3 protein was reduced in the rostral caudate-putamen (rCPu), whereas other isoforms were either unchanged or up-regulated. GRK6 protein and mRNA were up-regulated in rCPu and nucleus accumbens. l-DOPA (25 mg/kg, twice daily for 10 days) failed to reverse changes caused by DA depletion, whereas D(2)/D(3) agonist pergolide (0.25 mg/kg daily for 10 days) restored normal levels of expression of GRK5 and 6. In rCPu, GRK2 protein was increased in most subcellular fractions by l-DOPA but not by DA depletion alone. Similarly, l-DOPA up-regulated arrestin3 in membrane fractions in both regions. GRK5 was down-regulated by l-DOPA in cCPu in the light membrane fraction, where this isoform is the most abundant. The data suggest that alterations in the expression and subcellular distribution of arrestins and GRKs contribute to pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. Thus, these proteins may be targets for antiparkinsonian therapy.
Figures





References
-
- Ahn S, Wei H, Garrison TR, Lefkowitz RJ. Reciprocal regulation of angiotensin receptor-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinases by beta-arrestins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 2004a;279:7807–7811. - PubMed
-
- Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Wei H, Lefkowitz RJ. Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004b;279:35518–35525. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Crutcher MD. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:266–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM47417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH062651/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077561/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY11500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- GM068857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062654/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM77561/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045117/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS045117/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM047417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MH62654/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM047417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

