Identifications of conserved 7-mers in 3'-UTRs and microRNAs in Drosophila
- PMID: 17996040
- PMCID: PMC2241842
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-432
Identifications of conserved 7-mers in 3'-UTRs and microRNAs in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous regulatory small RNAs which play an important role in posttranscriptional regulations by targeting mRNAs for cleavage or translational repression. The base-pairing between the 5'-end of miRNA and the target mRNA 3'-UTRs is essential for the miRNA:mRNA recognition. Recent studies show that many seed matches in 3'-UTRs, which are fully complementary to miRNA 5'-ends, are highly conserved. Based on these features, a two-stage strategy can be implemented to achieve the de novo identification of miRNAs by requiring the complete base-pairing between the 5'-end of miRNA candidates and the potential seed matches in 3'-UTRs.
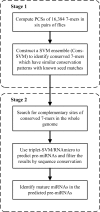
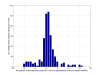
Results: We presented a new method, which combined multiple pairwise conservation information, to identify the frequently-occurred and conserved 7-mers in 3'-UTRs. A pairwise conservation score (PCS) was introduced to describe the conservation of all 7-mers in 3'-UTRs between any two Drosophila species. Using PCSs computed from 6 pairs of flies, we developed a support vector machine (SVM) classifier ensemble, named Cons-SVM and identified 689 conserved 7-mers including 63 seed matches covering 32 out of 38 known miRNA families in the reference dataset. In the second stage, we searched for 90 nt conserved stem-loop regions containing the complementary sequences to the identified 7-mers and used the previously published miRNA prediction software to analyze these stem-loops. We predicted 47 miRNA candidates in the genome-wide screen.
Conclusion: Cons-SVM takes advantage of the independent evolutionary information from the 6 pairs of flies and shows high sensitivity in identifying seed matches in 3'-UTRs. Combining the multiple pairwise conservation information by the machine learning approach, we finally identified 47 miRNA candidates in D. melanogaster.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

