Exploring the functional role of the CHRM2 gene in human cognition: results from a dense genotyping and brain expression study
- PMID: 17996044
- PMCID: PMC2198911
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-66
Exploring the functional role of the CHRM2 gene in human cognition: results from a dense genotyping and brain expression study
Abstract
Background: The CHRM2 gene, located on the long arm of chromosome 7 (7q31-35), is involved in neuronal excitability, synaptic plasticity and feedback regulation of acetylcholine release, and has been implicated in higher cognitive processing. The aim of this study is the identification of functional (non)coding variants underlying cognitive phenotypic variation.
Methods: We previously reported an association between polymorphisms in the 5'UTR regions of the CHRM2 gene and intelligence.. However, no functional variants within this area have currently been identified. In order to identify the relevant functional variant(s), we conducted a denser coverage of SNPs, using two independent Dutch cohorts, consisting of a children's sample (N = 371 ss; mean age 12.4) and an adult sample (N= 391 ss; mean age 37.6). For all individuals standardized intelligence measures were available. Subsequently, we investigated genotype-dependent CHRM2 gene expression levels in the brain, to explore putative enhancer/inhibition activity exerted by variants within the muscarinic acetylcholinergic receptor.
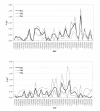
Results: Using a test of within-family association two of the previously reported variants - rs2061174, and rs324650 - were again strongly associated with intelligence (P < 0.01). A new SNP (rs2350780) showed a trend towards significance. SNP rs324650, is located within a short interspersed repeat (SINE). Although the function of short interspersed repeats remains contentious, recent research revealed potential functionality of SINE repeats in a gene-regulatory context. Gene-expression levels in post-mortem brain material, however were not dependent on rs324650 genotype.
Conclusion: Using a denser coverage of SNPs in the CHRM2 gene, we confirmed the 5'UTR regions to be most interesting in the context of intelligence, and ruled out other regions of this gene. Although no correlation between genomic variants and gene expression was found, it would be interesting to examine allele-specific effects on CHRM2 transcripts expression in much more detail, for example in relation to transcripts specific halve-life and their relation to LTP and memory.
Figures
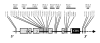
Similar articles
-
Association between the CHRM2 gene and intelligence in a sample of 304 Dutch families.Genes Brain Behav. 2006 Nov;5(8):577-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2006.00211.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2006. PMID: 17081262
-
Evidence of common and specific genetic effects: association of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene with alcohol dependence and major depressive syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Sep 1;13(17):1903-11. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh194. Epub 2004 Jun 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. PMID: 15229186
-
Genetic variation in cholinergic muscarinic-2 receptor gene modulates M2 receptor binding in vivo and accounts for reduced binding in bipolar disorder.Mol Psychiatry. 2011 Apr;16(4):407-18. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.24. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Mol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 20351719 Free PMC article.
-
Association of CHRM2 with IQ: converging evidence for a gene influencing intelligence.Behav Genet. 2007 Mar;37(2):265-72. doi: 10.1007/s10519-006-9131-2. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Behav Genet. 2007. PMID: 17160701
-
The genetics of alcoholism: identifying specific genes through family studies.Addict Biol. 2006 Sep;11(3-4):386-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2006.00035.x. Addict Biol. 2006. PMID: 16961766 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Effects of Ionizing Radiation on the Hippocampus: Linking Effects of the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Activation with Radiation Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12605. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212605. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830484 Free PMC article.
-
The ATXN1 and TRIM31 genes are related to intelligence in an ADHD background: evidence from a large collaborative study totaling 4,963 subjects.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011 Mar;156(2):145-57. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31149. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011. PMID: 21302343 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Oligofructose Alone or in Combination with 2'-Fucosyllactose Differentially Improves Recognition Memory and Hippocampal mRNA Expression.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 17;12(7):2131. doi: 10.3390/nu12072131. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32709093 Free PMC article.
-
The Xenorhabdus nematophila LrhA transcriptional regulator modulates production of γ-keto-N-acyl amides with inhibitory activity against mutualistic host nematode egg hatching.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Jul 24;90(7):e0052824. doi: 10.1128/aem.00528-24. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38916293 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the P3 event-related potential, its associated time-frequency components, and externalizing psychopathology.Psychophysiology. 2010 Jan 1;47(1):123-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00876.x. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Psychophysiology. 2010. PMID: 19674392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cherny SS, Cardon LR. General cognitive ability. . In: de Fries J, Plomin R, Fulker D, editor. Nature and nurture during middle childhood. Oxford , Blackwell Publishers; 1994. pp. 46–56.
-
- Plomin R, Turic DM, Hill L, Turic DE, Stephens M, Williams J, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC. A functional polymorphism in the succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 family, member A1) gene is associated with cognitive ability. Mol Psychiatry. 2004;9:582–586. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001441. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dick DM, Aliev F, Bierut L, Goate A, Rice J, Hinrichs A, Bertelsen S, Wang JC, Dunn G, Kuperman S, Schuckit M, Nurnberger J, Jr., Porjesz B, Beglieter H, Kramer J, Hesselbrock V. Linkage Analyses of IQ in the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) Sample. Behav Genet. 2006;36:77–86. doi: 10.1007/s10519-005-9009-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

