The FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) gene codes for a novel member of the non-heme dioxygenase superfamily
- PMID: 17996046
- PMCID: PMC2241624
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-8-23
The FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) gene codes for a novel member of the non-heme dioxygenase superfamily
Abstract
Background: Genetic variants in the FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) gene have been associated with an increased risk of obesity. However, the function of its protein product has not been experimentally studied and previously reported sequence similarity analyses suggested the absence of homologs in existing protein databases. Here, we present the first detailed computational analysis of the sequence and predicted structure of the protein encoded by FTO.
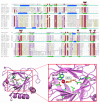
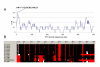
Results: We performed a sequence similarity search using the human FTO protein as query and then generated a profile using the multiple sequence alignment of the homologous sequences. Profile-to-sequence and profile-to-profile based comparisons identified remote homologs of the non-heme dioxygenase family.
Conclusion: Our analysis suggests that human FTO is a member of the non-heme dioxygenase (Fe(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases) superfamily. Amino acid conservation patterns support this hypothesis and indicate that both 2-oxoglutarate and iron should be important for FTO function. This computational prediction of the function of FTO should suggest further steps for its experimental characterization and help to formulate hypothesis about the mechanisms by which it relates to obesity in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of chicken fat mass and obesity associated (Fto) gene: fasting affects Fto expression.Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2012 Jan;42(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22019092
-
Loss-of-function mutation in the dioxygenase-encoding FTO gene causes severe growth retardation and multiple malformations.Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Jul;85(1):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19559399 Free PMC article.
-
An α-ketoglutarate conformational switch controls iron accessibility, activation, and substrate selection of the human FTO protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 18;121(25):e2404457121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2404457121. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38865275 Free PMC article.
-
The 'Fat Mass and Obesity Related' (FTO) gene: Mechanisms of Impact on Obesity and Energy Balance.Curr Obes Rep. 2015 Mar;4(1):73-91. doi: 10.1007/s13679-015-0143-1. Curr Obes Rep. 2015. PMID: 26627093 Review.
-
Local Charge Distributions, Electric Dipole Moments, and Local Electric Fields Influence Reactivity Patterns and Guide Regioselectivities in α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Non-heme Iron Dioxygenases.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jan 4;55(1):65-74. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00538. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34915695 Review.
Cited by
-
Fasting induced cytoplasmic Fto expression in some neurons of rat hypothalamus.PLoS One. 2013 May 6;8(5):e63694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063694. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23671692 Free PMC article.
-
RNAs and RNA-Binding Proteins in Immuno-Metabolic Homeostasis and Diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Aug 20;6:106. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00106. eCollection 2019. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 31482095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Where, When, and How: Context-Dependent Functions of RNA Methylation Writers, Readers, and Erasers.Mol Cell. 2019 May 16;74(4):640-650. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.025. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31100245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allelic polymorphism detected in the bovine FTO gene.Mol Biotechnol. 2011 Nov;49(3):257-62. doi: 10.1007/s12033-011-9400-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21479694
-
The association between FTO rs9939609 polymorphism and serum lipid profile in adult women.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 Nov 20;13(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00754-0. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 34801066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN, Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, Perry JR, Elliott KS, Lango H, Rayner NW, et al. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science. 2007;316:889–894. doi: 10.1126/science.1141634. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

