Advantages and mechanisms of polarity and cell shape determination in Caulobacter crescentus
- PMID: 17997127
- PMCID: PMC2175029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.09.007
Advantages and mechanisms of polarity and cell shape determination in Caulobacter crescentus
Abstract
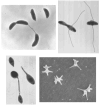
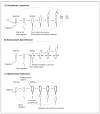
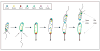
The tremendous diversity of bacterial cell shapes and the targeting of proteins and macromolecular complexes to specific subcellular sites strongly suggest that cellular organization provides important advantages to bacteria in their environment. Key advances have been made in the understanding of the mechanism and function of polarity and cell shape by studying the aquatic bacterium Caulobacter crescentus, whose cell cycle progression involves the ordered synthesis of different polar structures, and culminates in the biosynthesis of a thin polar cell envelope extension called the stalk. Recent results indicate that the important function of polar development is to maximize cell attachment to surfaces and to improve nutrient uptake by nonmotile and attached cells. Major progress has been made in understanding the regulatory network that coordinates polar development and morphogenesis and the role of polar localization of regulatory proteins.
Figures
References
-
- Cabeen MT, Jacobs-Wagner C. Bacterial cell shape. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3(8):601–10. - PubMed
-
- Shimkets LJ, Brun YV. Prokaryotic Development: Strategies to enhance survival. In: Brun YV, Shimkets LJ, editors. Prokaryotic Development. American Society for Microbiology; Washington, D.C: 2000. pp. 1–7.
-
- Wagner JK, Brun YV. Out on a limb: how the Caulobacter stalk can boost the study of bacterial cell shape. Mol Microbiol. 2007;64(1):28–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

