Essential role of mu opioid receptor in the regulation of delta opioid receptor-mediated antihyperalgesia
- PMID: 17997230
- PMCID: PMC2194644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.060
Essential role of mu opioid receptor in the regulation of delta opioid receptor-mediated antihyperalgesia
Abstract
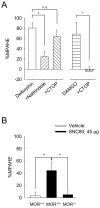
Analgesic effects of delta opioid receptor (DOR) -selective agonists are enhanced during persistent inflammation and arthritis. Although the underlying mechanisms are still unknown, membrane density of DOR was shown to be increased 72 h after induction of inflammation, an effect abolished in mu opioid receptor (MOR) -knockout (KO) mice [Morinville A, Cahill CM, Kieffer B, Collier B, Beaudet A (2004b) Mu-opioid receptor knockout prevents changes in delta-opioid receptor trafficking induced by chronic inflammatory pain. Pain 109:266-273]. In this study, we demonstrated a crucial role of MOR in DOR-mediated antihyperalgesia. Intrathecal administration of the DOR selective agonist deltorphin II failed to induce antihyperalgesic effects in MOR-KO mice, whereas it dose-dependently reversed thermal hyperalgesia in wild-type mice. The antihyperalgesic effects of deltorphin II were blocked by naltrindole but not d-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH(2) (CTOP) suggesting that this agonist was mainly acting through DOR. SNC80-induced antihyperalgesic effects in MOR-KO mice were also attenuated as compared with littermate controls. In contrast, kappa opioid receptor knockout did not affect deltorphin II-induced antihyperalgesia. As evaluated using mice lacking endogenous opioid peptides, the regulation of DOR's effects was also independent of beta-endorphin, enkephalins, or dynorphin opioids known to be released during persistent inflammation. We therefore conclude that DOR-mediated antihyperalgesia is dependent on MOR expression but that activation of MOR by endogenous opioids is probably not required.
Figures
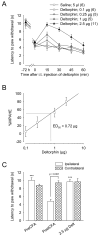

 ), pro-enkephalin-KO (pENK-KO; ○), β-endorphin-KO (β-END-KO; □), and pro-dynorphin-KO (pDYN-KO; △) mice. B, Comparative latencies to paw withdrawal (in s) in control littermates, pENK-, β-END-, and pDYN-KO mice before (0 min) and 15 min after intrathecal injection of deltorphin II (2.5 μg). Number in parenthesis indicates the number of animals in each group. #, p < 0.0001 when ipsilateral 0 min are compared with their respective ipsilateral preCFA; two-tailed unpaired t-test.
), pro-enkephalin-KO (pENK-KO; ○), β-endorphin-KO (β-END-KO; □), and pro-dynorphin-KO (pDYN-KO; △) mice. B, Comparative latencies to paw withdrawal (in s) in control littermates, pENK-, β-END-, and pDYN-KO mice before (0 min) and 15 min after intrathecal injection of deltorphin II (2.5 μg). Number in parenthesis indicates the number of animals in each group. #, p < 0.0001 when ipsilateral 0 min are compared with their respective ipsilateral preCFA; two-tailed unpaired t-test.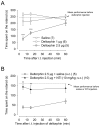
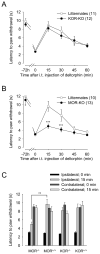
 ) received an equal volume of saline subcutaneously 15 min prior to deltorphin II. Mean performance before deltorphin (or before saline/NTI) injection represents the mean performance of all mice before treatment. **, p < 0.01 when compared to saline-pretreated group, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Number in parenthesis indicates the number of animals in each group.
) received an equal volume of saline subcutaneously 15 min prior to deltorphin II. Mean performance before deltorphin (or before saline/NTI) injection represents the mean performance of all mice before treatment. **, p < 0.01 when compared to saline-pretreated group, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Number in parenthesis indicates the number of animals in each group.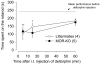
Similar articles
-
DPDPE-UK14,304 synergy is retained in mu opioid receptor knockout mice.Pain. 2003 Jul;104(1-2):209-17. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(03)00007-1. Pain. 2003. PMID: 12855331
-
Morphine priming in rats with chronic inflammation reveals a dichotomy between antihyperalgesic and antinociceptive properties of deltorphin.Neuroscience. 2007 Jan 5;144(1):263-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.077. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17055663
-
Two delta opioid receptor subtypes are functional in single ventral tegmental area neurons, and can interact with the mu opioid receptor.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:420-432. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.019. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28645621 Free PMC article.
-
The peripheral administration of a nitric oxide donor potentiates the local antinociceptive effects of a DOR agonist during chronic inflammatory pain in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;380(4):345-52. doi: 10.1007/s00210-009-0436-6. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19636536
-
The evolution of vertebrate opioid receptors.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(4):1247-69. doi: 10.2741/3306. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of δ-opioid receptor phosphorylation at threonine 161 attenuates morphine tolerance in rats with CFA-induced inflammatory hypersensitivity.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):182-92. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1216-8. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466129 Free PMC article.
-
Single Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Spinal Dmrt3 Neurons in Zebrafish and Mouse Identifies Distinct Subtypes and Reveal Novel Subpopulations Within the dI6 Domain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Dec 23;15:781197. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.781197. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 35002627 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Opioid Activity of Tyr1 -ψ[(Z)CF=CH]-Gly2 and Tyr1 -ψ[(S)/(R)-CF3 CH-NH]-Gly2 Leu-enkephalin Fluorinated Peptidomimetics.ChemMedChem. 2017 Apr 20;12(8):571-576. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201700103. Epub 2017 Apr 5. ChemMedChem. 2017. PMID: 28296145 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pharmacology of δ-Opioid Receptors.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Jul;68(3):631-700. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.008979. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27343248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of delta opioid agonist-induced antinociception by repeated morphine pretreatment in rhesus monkeys.Life Sci. 2010 Mar 13;86(11-12):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.01.006. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20096291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodnar RJ, Klein GE. Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2004. Peptides. 2005;26:2629–2711. - PubMed
-
- Brandt MR, Furness MS, Mello NK, Rice KC, Negus SS. Antinociceptive effects of delta-opioid agonists in Rhesus monkeys: effects on chemically induced thermal hypersensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001a;296:939–946. - PubMed
-
- Brandt MR, Furness MS, Rice KC, Fischer BD, Negus SS. Studies of tolerance and dependence with the delta-opioid agonist SNC80 in rhesus monkeys responding under a schedule of food presentation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001b;299:629–637. - PubMed
-
- Broom DC, Jutkiewicz EM, Folk JE, Traynor JR, Rice KC, Woods JH. Nonpeptidic delta-opioid receptor agonists reduce immobility in the forced swim assay in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:744–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

