Mutations in Drosophila Greatwall/Scant reveal its roles in mitosis and meiosis and interdependence with Polo kinase
- PMID: 17997611
- PMCID: PMC2065886
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030200
Mutations in Drosophila Greatwall/Scant reveal its roles in mitosis and meiosis and interdependence with Polo kinase
Abstract
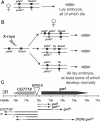
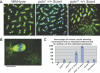
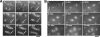
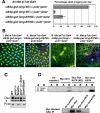
Polo is a conserved kinase that coordinates many events of mitosis and meiosis, but how it is regulated remains unclear. Drosophila females having only one wild-type allele of the polo kinase gene and the dominant Scant mutation produce embryos in which one of the centrosomes detaches from the nuclear envelope in late prophase. We show that Scant creates a hyperactive form of Greatwall (Gwl) with altered specificity in vitro, another protein kinase recently implicated in mitotic entry in Drosophila and Xenopus. Excess Gwl activity in embryos causes developmental failure that can be rescued by increasing maternal Polo dosage, indicating that coordination between the two mitotic kinases is crucial for mitotic progression. Revertant alleles of Scant that restore fertility to polo-Scant heterozygous females are recessive alleles or deficiencies of gwl; they show chromatin condensation defects and anaphase bridges in larval neuroblasts. One recessive mutant allele specifically disrupts a Gwl isoform strongly expressed during vitellogenesis. Females hemizygous for this allele are sterile, and their oocytes fail to arrest in metaphase I of meiosis; both homologues and sister chromatids separate on elongated meiotic spindles with little or no segregation. This allelic series of gwl mutants highlights the multiple roles of Gwl in both mitotic and meiotic progression. Our results indicate that Gwl activity antagonizes Polo and thus identify an important regulatory interaction of the cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Morgan DO. Cyclin-dependent kinases: engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:261–291. - PubMed
-
- Sunkel CE, Glover DM. polo, a mitotic mutant of Drosophila displaying abnormal spindle poles. J Cell Sci. 1988;89:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Llamazares S, Moreira A, Tavares A, Girdham C, Spruce BA, et al. polo encodes a protein kinase homolog required for mitosis in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991;5:2153–2165. - PubMed
-
- Glover DM. Polo kinase and progression through M phase in Drosophila: a perspective from the spindle poles. Oncogene. 2005;24:230–237. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai A, Dunphy WG. Purification and molecular cloning of Plx1, a Cdc25-regulatory kinase from Xenopus egg extracts. Science. 1996;273:1377–1380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

