Structure of the SOCS4-ElonginB/C complex reveals a distinct SOCS box interface and the molecular basis for SOCS-dependent EGFR degradation
- PMID: 17997974
- PMCID: PMC2225448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2007.09.016
Structure of the SOCS4-ElonginB/C complex reveals a distinct SOCS box interface and the molecular basis for SOCS-dependent EGFR degradation
Abstract
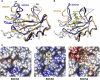
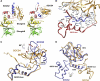
Tyrosine kinase signaling is tightly controlled by negative feedback inhibitors including suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS). SOCS assemble as SH2 domain substrate recognition modules in ElonginB/C-cullin ubiquitin ligases. In accordance, SOCS4 reduces STAT3 signaling from EGFR through increased receptor degradation. Variable C-termini in SOCS4-SOCS7 exclude these family members from a SOCS2-type domain arrangement in which a strictly conserved C terminus determines domain packing. The structure of the SOCS4-ElonginC-ElonginB complex reveals a distinct SOCS structural class. The N-terminal ESS helix functionally replaces the CIS/SOCS1-SOCS3 family C terminus in a distinct SH2-SOCS box interface that facilitates further interdomain packing between the extended N- and C-terminal regions characteristic for this subfamily. Using peptide arrays and calorimetry the STAT3 site in EGFR (pY(1092)) was identified as a high affinity SOCS4 substrate (K(D) = 0.5 microM) revealing a mechanism for EGFR degradation. SOCS4 also bound JAK2 and KIT with low micromolar affinity, whereas SOCS2 was specific for GH-receptor.
Figures


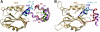
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the SOCS2-elongin C-elongin B complex defines a prototypical SOCS box ubiquitin ligase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 16;103(20):7637-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601638103. Epub 2006 May 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16675548 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for phosphotyrosine recognition by suppressor of cytokine signaling-3.Structure. 2006 Aug;14(8):1285-92. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2006.06.011. Structure. 2006. PMID: 16905102
-
The SOCS box domain of SOCS3: structure and interaction with the elonginBC-cullin5 ubiquitin ligase.J Mol Biol. 2008 Sep 12;381(4):928-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.038. Epub 2008 Jun 20. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18590740 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of the SOCS box.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008 Oct-Dec;19(5-6):371-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.08.006. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008. PMID: 18948053 Review.
-
The SOCS box-adapting proteins for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.IUBMB Life. 2012 Apr;64(4):316-23. doi: 10.1002/iub.1011. Epub 2012 Feb 23. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22362562 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of SH2 domains and phosphotyrosine signalling networks.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Sep 19;367(1602):2556-73. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0107. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22889907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for c-KIT inhibition by the suppressor of cytokine signaling 6 (SOCS6) ubiquitin ligase.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):480-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.173526. Epub 2010 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21030588 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS proteins in regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(17):3297-310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1619-y. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24705897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based design of a phosphotyrosine-masked covalent ligand targeting the E3 ligase SOCS2.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 10;14(1):6345. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41894-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37816714 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS Proteins as Regulators of Inflammatory Responses Induced by Bacterial Infections: A Review.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 12;8:2431. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02431. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29312162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abagyan R.A., Totrov M., Kuznetsov D. ICM: a new method for protein modeling and design: applications to docking and structure prediction from the distorted native conformation. J. Comput. Chem. 1994;15:488–506.
-
- Arbouzova N.I., Zeidler M.P. JAK/STAT signalling in Drosophila: insights into conserved regulatory and cellular functions. Development. 2006;133:2605–2616. - PubMed
-
- Babon J.J., McManus E.J., Yao S., DeSouza D.P., Mielke L.A., Sprigg N.S., Willson T.A., Hilton D.J., Nicola N.A., Baca M. The structure of SOCS3 reveals the basis of the extended SH2 domain function and identifies an unstructured insertion that regulates stability. Mol. Cell. 2006;22:205–216. - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Barber D.L., Beattie B.K., Mason J.M., Nguyen M.H., Yoakim M., Neel B.G., D'Andrea A.D., Frank D.A. A common epitope is shared by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 (STAT5) and the phosphorylated erythropoietin receptor: implications for the docking model of STAT activation. Blood. 2001;97:2230–2237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

