In vivo dynamic imaging of myocardial cell death using 99mTc-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I in a rat model of ischemia and reperfusion
- PMID: 17998092
- PMCID: PMC2515710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.07.013
In vivo dynamic imaging of myocardial cell death using 99mTc-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I in a rat model of ischemia and reperfusion
Abstract
Objectives: This study was designed to investigate the capability of a small-animal SPECT imager, FastSPECT II, for dynamic rat heart imaging and to characterize the in vivo kinetic properties of 99mTc-C2A-glutathione-s-transferase (GST), a molecular probe targeting apoptosis and necrosis, in detecting cell death in ischemic-reperfused rat hearts.
Methods: C2A-GST was radiolabeled with 99mTc via 2-iminothiolane thiolation. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion was induced by 30-min ligation of the left coronary artery followed by 120-min reperfusion in seven rats. FastSPECT II cardiac images of 99mTc-C2A-GST in list-mode acquisition were recorded for 2 h using FastSPECT II.
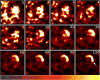
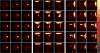
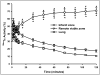
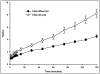
Results: Tomographic images showed a focal radioactive accumulation (hot spot) in the lateral and anterior walls of the left ventricle. The hot spot was initially visualized 10 min after injection and persisted on the 2-h images. Quantitative analysis demonstrated that the hot-spot radioactivity increased significantly within 30 min postinjection and experienced no washout up to the end of the 2-h study. The ratio of the hot spot/viable myocardium was 4.52+/-0.24, and infarct-to-lung ratio was 8.22+/-0.63 at 2 h postinjection. The uptake of 99mTc-C2A-GST in the infarcted myocardium was confirmed by triphenyl tetrazolium chloride staining and autoradiography analysis.
Conclusions: FastSPECT II allows quantitative dynamic imaging and functional determination of radiotracer kinetics in rat hearts. An in vivo kinetic profile of 99mTc-C2A-GST in the ischemic-reperfused rat heart model was characterized successfully. The pattern of accelerated 99mTc-C2A-GST uptake in the ischemic area at risk after reperfusion may be useful in detecting and quantifying ongoing myocardial cell loss induced by ischemia-reperfusion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SPECT imaging of myocardial infarction using 99mTc-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I in a porcine ischemia-reperfusion model.Nucl Med Biol. 2007 Nov;34(8):917-23. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.06.014. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Nucl Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17998093
-
Quantitative analysis of [99mTc]C2A-GST distribution in the area at risk after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion using a compartmental model.Nucl Med Biol. 2007 Nov;34(8):897-905. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Nucl Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17998091
-
Imaging acute cardiac cell death: temporal and spatial distribution of 99mTc-labeled C2A in the area at risk after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion.J Nucl Med. 2007 Jun;48(6):1031-6. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.106.037754. J Nucl Med. 2007. PMID: 17536109
-
99mTc-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I as a target-specific molecular probe for noninvasive imaging of acute myocardial infarction.J Nucl Med. 2006 Aug;47(8):1367-74. J Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 16883018
-
4-[18F]Fluorobenzoyl-C2A domain of synaptotagmin I-glutathione-S-transferase.2011 May 27 [updated 2011 Aug 4]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 May 27 [updated 2011 Aug 4]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21834184 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of chemotherapy response in VX2 rabbit lung cancer with 18F-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I.J Nucl Med. 2011 Apr;52(4):592-9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.081588. Epub 2011 Mar 18. J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 21421722 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical Imaging in Experimental Models of Cardiovascular Disease.Circ Res. 2022 Jun 10;130(12):1851-1868. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.320306. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35679370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Experimental Rat Model for the In Vivo Assessment of Myocardial Ischemia Based on Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography.In Vivo. 2023 Mar-Apr;37(2):649-654. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13124. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 36881049 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Has a Regenerative Effect in Ischemic Myocardium: An Experimental Rat Model Evaluated by SPECT-CT Assessment.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 12;14(4):401. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14040401. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396441 Free PMC article.
-
Lantibiotics as probes for phosphatidylethanolamine.Amino Acids. 2011 Nov;41(5):1071-9. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0386-9. Epub 2009 Nov 22. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 21573677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gottlieb RA, Engler RL. Apoptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;874:412–6. - PubMed
-
- Buja LM, Entman ML. Modes of myocardial cell injury and cell death in ischemic heart disease. Circulation. 1998;98:1355–7. - PubMed
-
- Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RC, LaFace DM, et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med. 1995;182:1545–56. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

