Temporal regulation of interleukin-12p70 (IL-12p70) and IL-12-related cytokines in splenic dendritic cell subsets during Leishmania donovani infection
- PMID: 17998312
- PMCID: PMC2223655
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00643-07
Temporal regulation of interleukin-12p70 (IL-12p70) and IL-12-related cytokines in splenic dendritic cell subsets during Leishmania donovani infection
Abstract
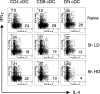
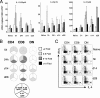
Dendritic cells (DC) play an essential role in initiating and directing T-cell responses, in part by production of interleukin-12p70 (IL-12p70), IL-23, and IL-27. However, comparative studies on the capacity for cytokine production of DC subsets are rare. Here, we compare splenic CD8alpha+, CD4+, and double-negative (DN) DC, isolated 5 h to 28 days after Leishmania donovani infection, for (i) production of IL-12p70, (ii) accumulation of IL-12/23p40, IL-12p35, IL-23p19, and IL-27p28 mRNAs, and (iii) their capacity to direct CD4+ T-cell differentiation. At 5 h, conventional DC (cDC) accumulated mRNA for IL-12/23p40 (CD8alpha>CD4>DN), IL-23p19 (CD4>CD8alpha>DN), and IL-27p28 (CD8alpha>CD4>DN), in an infection dose-dependent manner. IL-12p70 was restricted to CD8alpha+ cDC, reflecting the subset-specific accumulation of IL-12p35 mRNA. In contrast, cDC from mice infected for 14 to 28 days accumulated little mRNA for IL-12p40 and IL-12p19, though IL-27p28 mRNA remained detectable (CD8alpha>DN>CD4). IL-12p70 secretion by CD8alpha+ cDC was also absent, reflecting deficient IL-12/23p40, rather than IL-12p35, mRNA accumulation. The capacity of CD8alpha+ cDC isolated early after infection to direct Th1 cell differentiation was mediated through IL-12/23p40, whereas this ability in CD4+ and DN cDC was independent of IL-12/23p40 and did not result from overexpression of Delta 4 Notch-like ligand. However, DN cDC produced gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and also contained a rare population of CD11c(hi) DX5+ IFN-gamma-producing cells. Our data illustrate the extensive diversity in, and temporal regulation of, splenic cDC subsets during infection and suggest caution in interpreting data obtained with unfractionated or minimally purified DC.
Figures


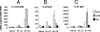

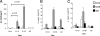

Similar articles
-
Reciprocal changes in CD11c+CD11b+ and CD11c+CD8α+ dendritic cell subsets determine protective or permissive immune response in murine experimental VL.Vaccine. 2020 Jan 10;38(2):355-365. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 31648908
-
Modulation of CD11C+ splenic dendritic cell functions in murine visceral leishmaniasis: correlation with parasite replication in the spleen.Immunology. 2000 Feb;99(2):305-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00939.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 10692051 Free PMC article.
-
Regional differences in the cellular immune response to experimental cutaneous or visceral infection with Leishmania donovani.Infect Immun. 1998 Jan;66(1):18-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.1.18-27.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9423834 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen presentation capacity and cytokine production by murine splenic dendritic cell subsets upon Salmonella encounter.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 1;169(1):108-16. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.1.108. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12077235
-
[Effect of neonatal BCG vaccination on phenotype and function of splenic dendritic cells of BALB/c mice].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Oct;46(10):784-8. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 19099886 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Natural killer cells in experimental and human leishmaniasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 May 29;2:69. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00069. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spleen-resident CD4+ and CD4- CD8α- dendritic cell subsets differ in their ability to prime invariant natural killer T lymphocytes.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026919. Epub 2011 Oct 31. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22066016 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-27 Functional Duality Balances Leishmania Infectivity and Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 7;11:1573. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01573. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Cytokines in Experimental and Human Visceral Leishmaniasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 18;11:624009. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.624009. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33680991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune evasion by Yersinia enterocolitica: differential targeting of dendritic cell subpopulations in vivo.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Nov 24;6(11):e1001212. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001212. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 21124820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artis, D., L. M. Johnson, K. Joyce, C. Saris, A. Villarino, C. A. Hunter, and P. Scott. 2004. Early IL-4 production governs the requirement for IL-27-WSX-1 signaling in the development of protective Th1 cytokine responses following Leishmania major infection. J. Immunol. 1724672-4675. - PubMed
-
- Ato, M., S. Stager, C. R. Engwerda, and P. M. Kaye. 2002. Defective CCR7 expression on dendritic cells contributes to the development of visceral leishmaniasis. Nat. Immunol. 31185-1191. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid, Y., B. Butcher, and D. L. Sacks. 1998. Analysis of cytokine production by inflammatory mouse macrophages at the single-cell level: selective impairment of IL-12 induction in Leishmania-infected cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 281389-1400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

