Wdr82 is a C-terminal domain-binding protein that recruits the Setd1A Histone H3-Lys4 methyltransferase complex to transcription start sites of transcribed human genes
- PMID: 17998332
- PMCID: PMC2223426
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01356-07
Wdr82 is a C-terminal domain-binding protein that recruits the Setd1A Histone H3-Lys4 methyltransferase complex to transcription start sites of transcribed human genes
Abstract
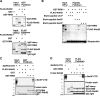
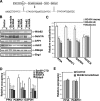
Histone H3-Lys4 trimethylation is associated with the transcription start site of transcribed genes, but the molecular mechanisms that control this distribution in mammals are unclear. The human Setd1A histone H3-Lys4 methyltransferase complex was found to physically associate with the RNA polymerase II large subunit. The Wdr82 component of the Setd1A complex interacts with the RNA recognition motif of Setd1A and additionally binds to the Ser5-phosphorylated C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, which is involved in initiation of transcription, but does not bind to an unphosphorylated or Ser2-phosphorylated C-terminal domain. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis revealed that Setd1A is localized near the transcription start site of expressed genes. Small interfering RNA-mediated depletion of Wdr82 leads to decreased Setd1A expression and occupancy at transcription start sites and reduced histone H3-Lys4 trimethylation at these sites. However, neither RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) occupancy nor target gene expression levels are altered following Wdr82 depletion. Hence, Wdr82 is required for the targeting of Setd1A-mediated histone H3-Lys4 trimethylation near transcription start sites via tethering to RNA polymerase II, an event that is a consequence of transcription initiation. These results suggest a model for how the mammalian RNAP II machinery is linked with histone H3-Lys4 histone methyltransferase complexes at transcriptionally active genes.
Figures

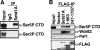

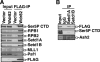
References
-
- Bernstein, B. E., M. Kamal, K. Lindblad-Toh, S. Bekiranov, D. K. Bailey, D. J. Huebert, S. McMahan, E. K. Karlsson, E. J. Kulbokas, T. R. Gingeras, S. L. Schreiber, and E. S. Lander. 2005. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell 120169-181. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, B. E., T. S. Mikkelsen, X. Xie, M. Kamal, D. J. Huebert, J. Cuff, B. Fry, A. Meissner, M. Wernig, K. Plath, R. Jaenisch, A. Wagschal, R. Reil, S. L. Schreiber, and E. S. Lander. 2006. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell 125315-326. - PubMed
-
- Couture, J.-F., E. Collazo, and R. C. Trievel. 2006. Molecular recognition of histone H3 by the WD40 protein WDR5. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13698-703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
