ANCCA, an estrogen-regulated AAA+ ATPase coactivator for ERalpha, is required for coregulator occupancy and chromatin modification
- PMID: 17998543
- PMCID: PMC2084297
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705814104
ANCCA, an estrogen-regulated AAA+ ATPase coactivator for ERalpha, is required for coregulator occupancy and chromatin modification
Abstract
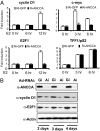
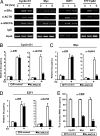
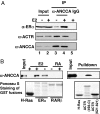
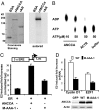
AAA+ proteins play crucial roles in diverse biological processes via their ATPase-driven remodeling of macromolecular complexes. Here we report our identification of an evolutionarily conserved AAA+ protein, ANCCA/pro2000, endowed with a bromodomain that is strongly induced by estrogen in human breast cancer cells and is a direct target of protooncogene ACTR/AIB1/SRC-3. We found that ANCCA associates directly with estrogen-bound estrogen receptor (ER) alpha and ACTR. It is selectively recruited, upon estrogen stimulation, to a subset of ERalpha target genes including cyclin D1, c-myc, and E2F1 and is required for their estrogen-induced expression as well as breast cancer cell proliferation. Further studies indicate that ANCCA binds and hydrolyzes ATP and is critical for recruitment of coregulator CBP and histone hyperacetylation at the ER target chromatin. Moreover, mutations at the ATP binding motifs rendered ANCCA defective as a coactivator in mediating estrogen induction of gene expression. Together, our findings reveal an unexpected layer of regulatory mechanism in hormone signaling mediated by ANCCA and suggest that hormone-induced assembly of transcriptional coregulator complexes at chromatin is a process facilitated by AAA+ ATPase proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
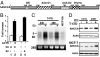
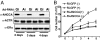
Similar articles
-
Chromatin loading of E2F-MLL complex by cancer-associated coregulator ANCCA via reading a specific histone mark.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;30(22):5260-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00484-10. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20855524 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulated E2F and the AAA+ coregulator ANCCA drive proto-oncogene ACTR/AIB1 overexpression in breast cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Feb;8(2):183-93. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0095. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20124470
-
Kinesin family deregulation coordinated by bromodomain protein ANCCA and histone methyltransferase MLL for breast cancer cell growth, survival, and tamoxifen resistance.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Apr;12(4):539-49. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0459. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24391143 Free PMC article.
-
ANCCA/ATAD2 overexpression identifies breast cancer patients with poor prognosis, acting to drive proliferation and survival of triple-negative cells through control of B-Myb and EZH2.Cancer Res. 2010 Nov 15;70(22):9402-12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1199. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20864510 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor alpha phosphorylation and its functional impact in human breast cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 3:264-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25597633 Review.
Cited by
-
A machine learning heuristic to identify biologically relevant and minimal biomarker panels from omics data.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S1-S2. Epub 2015 Jan 15. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25923811 Free PMC article.
-
ATPase family AAA domain-containing protein 2 (ATAD2): From an epigenetic modulator to cancer therapeutic target.Theranostics. 2023 Jan 1;13(2):787-809. doi: 10.7150/thno.78840. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 36632213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization Analysis Reveals Significantly Enriched Pathways in Canine Oral Melanoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 12;9:1397. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01397. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31921654 Free PMC article.
-
miR-372 down-regulates the oncogene ATAD2 to influence hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2014 Feb 19;14:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-107. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24552534 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis of the Clinical Value and Biological Function of ATAD2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 5;2020:8657468. doi: 10.1155/2020/8657468. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32462022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hewitt SC, Harrell JC, Korach KS. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:285–308. - PubMed
-
- Dahlman-Wright K, Cavailles V, Fuqua SA, Jordan VC, Katzenellenbogen JA, Korach KS, Maggi A, Muramatsu M, Parker MG, Gustafsson JA. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:773–781. - PubMed
-
- Acevedo ML, Kraus WL. Essays Biochem. 2004;40:73–88. - PubMed
-
- Smith CL, O'Malley BW. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:45–71. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Kinyamu HK, Archer TK. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

