Contribution of SHANK3 mutations to autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 17999366
- PMCID: PMC2276348
- DOI: 10.1086/522590
Contribution of SHANK3 mutations to autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
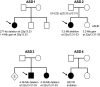
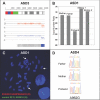
Mutations in SHANK3, which encodes a synaptic scaffolding protein, have been described in subjects with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD). To assess the quantitative contribution of SHANK3 to the pathogenesis of autism, we determined the frequency of DNA sequence and copy-number variants in this gene in 400 ASD-affected subjects ascertained in Canada. One de novo mutation and two gene deletions were discovered, indicating a contribution of 0.75% in this cohort. One additional SHANK3 deletion was characterized in two ASD-affected siblings from another collection, which brings the total number of published mutations in unrelated ASD-affected families to seven. The combined data provide support that haploinsufficiency of SHANK3 can cause a monogenic form of autism in sufficient frequency to warrant consideration in clinical diagnostic testing.
Figures
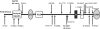
References
Web Resources
-
- Database of Genomic Variants, http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/
-
- DECIPHER, http://www.sanger.ac.uk/PostGenomics/decipher/ (for the Database of Chromosomal Imbalance and Phenotype in Humans using Ensembl Resources) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for autism, fragile X syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, 22q13.3 deletion syndrome, and Rett syndrome)
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
-
- Xu J, Zwaigenbaum L, Szatmari P, Scherer SW (2004) Molecular cytogenetics of autism. Curr Genomics 5:347–36410.2174/1389202043349246 - DOI
-
- Jacquemont ML, Sanlaville D, Redon R, Raoul O, Cormier-Daire V, Lyonnet S, Amiel J, Le Merrer M, Heron D, de Blois MC, et al (2006) Array-based comparative genomic hybridisation identifies high frequency of cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in patients with syndromic autism spectrum disorders. J Med Genet 43:843–84910.1136/jmg.2006.043166 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

