Therapeutic perspectives for the treatment of Huntington's disease: treating the whole body
- PMID: 17999380
- PMCID: PMC2657556
- DOI: 10.14670/HH-23.237
Therapeutic perspectives for the treatment of Huntington's disease: treating the whole body
Abstract
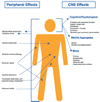
Huntington's disease (HD) is a tremendously debilitating disorder that strikes relatively young individuals and progresses rapidly over the next ten to fifteen years inducing a loss of cognitive and motor skills and eventually death occurs. The primary locus of the disorder is a polyglutamine expansion of the protein product of the huntingtin (htt) gene. The htt protein appears to be a scaffolding protein that orchestrates the complex assembly of multiple intracellular proteins involved in multiple processes, including vesicular movement and cell metabolism. The htt protein is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues but the predominance of the interest in the pathology lies in its effects on the central nervous system (CNS). Most of the current therapeutics for HD thus have been targeted at preventing neuronal damage in the CNS, however, a considerable body of evidence has been accumulating to suggest that the maintenance of a healthy nervous system is tightly linked with peripheral physiological health. Therefore treatment of both the peripheral and central pathophysiologies of HD could form the basis of a more effective HD therapeutic strategy.
Figures
References
-
- Anden NE, Dalen P, Johansson B. Baclofen and lithium in Huntington’s chorea. Lancet. 1973;2:93. - PubMed
-
- Andrich J, Saft C, Gerlach M, Schneider B, Arz A, Kuhn W, Muller T. Coenzyme Q10 serum levels in Huntington’s disease. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2004;68:111–116. - PubMed
-
- Arenas J, Campos Y, Ribacoba R, Martin MA, Rubio JC, Ablanedo P, Cabello A. Complex I defect in muscle from patients with Huntington’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1998;43:397–400. - PubMed
-
- Bachoud-Levi AC, Gaura V, Brugieres P, Lefaucheur JP, Boisse MF, Maison P, Baudic S, Ribeiro MJ, Bourdet C, Remy P, Remy P, Cesaro P, Hantraye P, Peschanski M. Effect of fetal neural transplants in patients with Huntington’s disease 6 years after surgery: a long-term follow-up study. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Barker RA, Rosser AE. Neural transplantation therapies for Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases. Drug Discov. Today. 2001;6:575–582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
