Inhibition of HIV-1 transmission in trans from dendritic cells to CD4+ T lymphocytes by natural antibodies to the CRD domain of DC-SIGN purified from breast milk and intravenous immunoglobulins
- PMID: 17999675
- PMCID: PMC2433318
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02717.x
Inhibition of HIV-1 transmission in trans from dendritic cells to CD4+ T lymphocytes by natural antibodies to the CRD domain of DC-SIGN purified from breast milk and intravenous immunoglobulins
Abstract
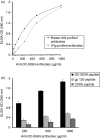
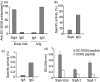
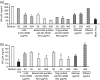
The present study demonstrates that human breast milk and normal human polyclonal immunoglobulins purified from plasma [intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg)] contain functional natural immunoglobulin A (IgA) and IgG antibodies directed against the carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) domain of the dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN) molecule, which is involved in the binding of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 to dendritic cells (DCs). Antibodies to DC-SIGN CRD were affinity-purified on a matrix to which a synthetic peptide corresponding to the N-terminal CRD domain (amino-acid 342-amino-acid 371) had been coupled. The affinity-purified antibodies bound to the DC-SIGN peptide and to the native DC-SIGN molecule expressed by HeLa DC-SIGN+ cells and immature monocyte-derived dendritic cells (iMDDCs), in a specific and dose-dependent manner. At an optimal dose of 200 microg/ml, natural antibodies to DC-SIGN CRD peptide purified from breast milk and IVIg stained 25 and 20% of HeLa DC-SIGN+ cells and 32 and 12% of iMDDCs, respectively. Anti-DC-SIGN CRD peptide antibodies inhibited the attachment of virus to HeLa DC-SIGN by up to 78% and the attachment to iMDDCs by only 20%. Both breast milk- and IVIg-derived natural antibodies to the CRD peptide inhibited 60% of the transmission in trans of HIV-1(JRCSF), an R5-tropic strain, from iMDDCs to CD4+ T lymphocytes. Taken together, these observations suggest that the attachment of HIV to DCs and transmission in trans to autologous CD4+ T lymphocytes occur through two independent mechanisms. Our data support a role of natural antibodies to DC-SIGN in the modulation of postnatal HIV transmission through breast-feeding and in the natural host defence against HIV-1 in infected individuals.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficient capture of antibody neutralized HIV-1 by cells expressing DC-SIGN and transfer to CD4+ T lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2007 Mar 1;178(5):3177-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.3177. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17312166
-
Lewis X component in human milk binds DC-SIGN and inhibits HIV-1 transfer to CD4+ T lymphocytes.J Clin Invest. 2005 Nov;115(11):3256-64. doi: 10.1172/JCI25105. Epub 2005 Oct 20. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16239964 Free PMC article.
-
DC-SIGN (dendritic cell-specific ICAM-grabbing non-integrin) and DC-SIGN-related (DC-SIGNR): friend or foe?Clin Sci (Lond). 2003 Apr;104(4):437-46. Clin Sci (Lond). 2003. PMID: 12653690 Review.
-
Mucin 6 in seminal plasma binds DC-SIGN and potently blocks dendritic cell mediated transfer of HIV-1 to CD4(+) T-lymphocytes.Virology. 2009 Sep 1;391(2):203-11. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.06.011. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19682628
-
Viral piracy: HIV-1 targets dendritic cells for transmission.Curr HIV Res. 2006 Apr;4(2):169-76. doi: 10.2174/157016206776055020. Curr HIV Res. 2006. PMID: 16611055 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of carbohydrate-binding agents as therapeutics against enveloped viruses.Med Res Rev. 2012 Mar;32(2):349-87. doi: 10.1002/med.20216. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Med Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 20577974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Trans Infection of CD4(+) T Cells by Professional Antigen Presenting Cells.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:164203. doi: 10.1155/2013/164203. Epub 2013 May 7. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 24278768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bifunctional CD4-DC-SIGN fusion proteins demonstrate enhanced avidity to gp120 and inhibit HIV-1 infection and dissemination.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Sep;56(9):4640-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00623-12. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22687513 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activity of candidate microbicides against early steps of HIV-1 infection upon complement virus opsonization.AIDS Res Ther. 2010 Jun 14;7:16. doi: 10.1186/1742-6405-7-16. AIDS Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20546571 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type I Pathogenesis: Threat or Opportunity?Adv Virol. 2016;2016:9852494. doi: 10.1155/2016/9852494. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Adv Virol. 2016. PMID: 26981123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coutinho A, Kazatchkine MD, Avrameas S. Natural autoantibodies. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:812–8. - PubMed
-
- Hayakawa K, Asano M, Shinton SA, Gui M, Allman D, Stewart CL, Silver J, Hardy RR. Positive selection of natural autoreactive B cells. Science. 1999;285:113–6. - PubMed
-
- Ochsenbein AF, Fehr T, Lutz C, Suter M, Brombacher F, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel RM. Control of early viral and bacterial distribution and disease by natural antibodies. Science. 1999;286:2156–9. - PubMed
-
- Bystryn JC, Jiao D. IVIg selectively and rapidly decreases circulating pathogenic autoantibodies in pemphigus vulgaris. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:601–7. - PubMed
-
- Katz U, Kishner I, Magalashvili D, Shoenfeld Y, Achiron A. Long term safety of IVIg therapy in multiple sclerosis: 10 years experience. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:513–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

