Individual space-time activity-based modelling of infectious disease transmission within a city
- PMID: 17999949
- PMCID: PMC2607451
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2007.1218
Individual space-time activity-based modelling of infectious disease transmission within a city
Abstract
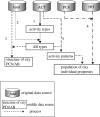
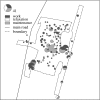
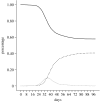
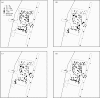
This paper provides an example of the application of an individual space-time activity-based model (ISTAM) to the simulation of the transmission of infectious disease in Eemnes, a city in The Netherlands. Four questions were addressed: (i) how to build the whole population at the city level, (ii) how to build the structure of the activity bundles for the city, (iii) how to assign daily activity patterns to each individual, and (iv) how to simulate within-AB transmission. The model was calibrated and examples of simulation results such as dynamics of the population during a whole day, infection distribution and network analysis are presented.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson R.M, May R.M. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1992. Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control.
-
- Arentze T, Timmermans H. Parametric action decision trees: incorporating continuous attribute variables into rule-based models of discrete choice. Transport. Res. B: Methodol. 2007;41:772–783. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2007.01.001. - DOI
-
- Baldassare M. Human spatial behavior. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1978;4:29–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.so.04.080178.000333. - DOI
-
- Batty M. Agent-based pedestrian modelling. In: Longley P.A, Batty M, editors. Advanced spatial analysis: the CASA book of GIS. ESRI Press; Redlands, CA: 2003. pp. 81–105.
-
- Batty M. Agents, cells, and cities: new representational models for simulating multiscale urban dynamics. Environ. Plann. A. 2005a;37:1373–1394. doi: 10.1068/a3784. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
