The mechanism of action of beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methylcytidine involves a second metabolic pathway leading to beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methyluridine 5'-triphosphate, a potent inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- PMID: 17999967
- PMCID: PMC2224766
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01184-07
The mechanism of action of beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methylcytidine involves a second metabolic pathway leading to beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methyluridine 5'-triphosphate, a potent inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Abstract
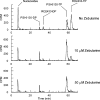
beta-D-2'-Deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methylcytidine (PSI-6130) is a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA replication in an HCV replicon assay. The 5'-triphosphate of PSI-6130 is a competitive inhibitor of the HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and acts as a nonobligate chain terminator. Recently, it has been shown that the metabolism of PSI-6130 also results in the formation of the 5'-triphosphate of the uridine congener, beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methyluridine (PSI-6206; RO2433). Here we show that the formation of the 5'-triphosphate of RO2433 (RO2433-TP) requires the deamination of PSI-6130 monophosphate and that RO2433 monophosphate is subsequently phosphorylated to the corresponding di- and triphosphates by cellular UMP-CMP kinase and nucleoside diphosphate kinase, respectively. RO2433-TP is a potent inhibitor of the HCV RdRp; however, both enzymatic and cell-based assays show that PSI-6130 triphosphate is a more potent inhibitor of the HCV RdRp than RO2433-TP.
Figures
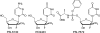

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the metabolic activation of hepatitis C virus nucleoside inhibitor beta-D-2'-Deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methylcytidine (PSI-6130) and identification of a novel active 5'-triphosphate species.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 12;282(41):29812-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705274200. Epub 2007 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17698842
-
Mechanism of activation of beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-c-methylcytidine and inhibition of hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA polymerase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Feb;51(2):503-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00400-06. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17101674 Free PMC article.
-
Selected replicon variants with low-level in vitro resistance to the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor PSI-6130 lack cross-resistance with R1479.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Dec;52(12):4356-69. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00444-08. Epub 2008 Oct 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18838588 Free PMC article.
-
PSI-7851, a pronucleotide of beta-D-2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-2'-C-methyluridine monophosphate, is a potent and pan-genotype inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Aug;54(8):3187-96. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00399-10. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20516278 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to mericitabine, a nucleoside analogue inhibitor of HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.Antivir Ther. 2012;17(3):411-23. doi: 10.3851/IMP2088. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Antivir Ther. 2012. PMID: 22402762 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys.Nature. 2016 Mar 17;531(7594):381-5. doi: 10.1038/nature17180. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26934220 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights in antiviral drug research: antivirals at the horizon.Med Res Rev. 2013 Nov;33(6):1215-48. doi: 10.1002/med.21256. Epub 2012 May 2. Med Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 22553111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular effects of the Hepatitis C virus nucleoside polymerase inhibitor RO5855 (Mericitabine Parent) and Ribavirin in combination.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 May;58(5):2614-25. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02250-13. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24550342 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Design of Antivirals against Envelope Glycoprotein of Dengue Virus.Viruses. 2020 Mar 26;12(4):367. doi: 10.3390/v12040367. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32225021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Antiviral Activity of a Series of 2'-C-Methyl-4'-thionucleoside Monophosphate Prodrugs.Molecules. 2020 Nov 6;25(21):5165. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215165. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33171951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaoui-Lsmaili, M. H., M. Hamel, L. L'Heureux, O. Nicolas, D. Bilimoria, P. Labonte, S. Mounir, and R. F. Rando. 2000. The hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity and susceptibility to inhibitors is modulated by metal cations. J. Hum. Virol. 3:306-316. - PubMed
-
- Alter, M. J., D. Kruszon-Moran, O. V. Nainan, G. M. McQuillan, F. Gao, L. A. Moyer, R. A. Kaslow, and H. S. Margolis. 1999. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N. Engl. J. Med. 341:556-562. - PubMed
-
- Blight, K. J., A. A. Kolykhalov, and C. M. Rice. 2000. Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290:1972-1974. - PubMed
-
- Carroll, S. S., J. E. Tomassini, M. Bosserman, K. Getty, M. W. Stahlhut, A. B. Eldrup, B. Bhat, D. Hall, A. L. Simcoe, R. LaFemina, C. A. Rutkowski, B. Wolanski, Z. Yang, G. Migliaccio, R. De Francesco, L. C. Kuo, M. MacCoss, and D. B. Olsen. 2003. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus RNA replication by 2′-modified nucleoside analogs. J. Biol. Chem. 278:11979-11984. - PubMed
-
- Clark, J. L., J. C. Mason, L. Hollecker, L. J. Stuyver, P. M. Tharnish, T. R. McBrayer, M. J. Otto, P. A. Furman, R. F. Schinazi, and K. A. Watanabe. 2006. Synthesis and antiviral activity of 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methyl purine nucleosides as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus RNA replication. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16:1712-1715. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

