The process of displacing the single-stranded DNA-binding protein from single-stranded DNA by RecO and RecR proteins
- PMID: 18000001
- PMCID: PMC2248737
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm1004
The process of displacing the single-stranded DNA-binding protein from single-stranded DNA by RecO and RecR proteins
Abstract
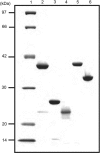
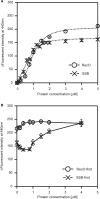
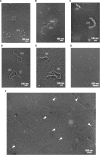
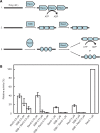
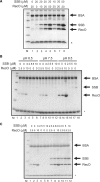
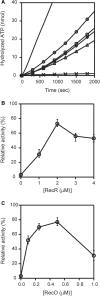
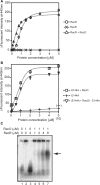
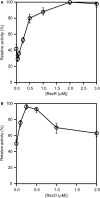
The regions of single-stranded (ss) DNA that result from DNA damage are immediately coated by the ssDNA-binding protein (SSB). RecF pathway proteins facilitate the displacement of SSB from ssDNA, allowing the RecA protein to form protein filaments on the ssDNA region, which facilitates the process of recombinational DNA repair. In this study, we examined the mechanism of SSB displacement from ssDNA using purified Thermus thermophilus RecF pathway proteins. To date, RecO and RecR are thought to act as the RecOR complex. However, our results indicate that RecO and RecR have distinct functions. We found that RecR binds both RecF and RecO, and that RecO binds RecR, SSB and ssDNA. The electron microscopic studies indicated that SSB is displaced from ssDNA by RecO. In addition, pull-down assays indicated that the displaced SSB still remains indirectly attached to ssDNA through its interaction with RecO in the RecO-ssDNA complex. In the presence of both SSB and RecO, the ssDNA-dependent ATPase activity of RecA was inhibited, but was restored by the addition of RecR. Interestingly, the interaction of RecR with RecO affected the ssDNA-binding properties of RecO. These results suggest a model of SSB displacement from the ssDNA by RecF pathway proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein interactions in genetic recombination in Escherichia coli. Interactions involving RecO and RecR overcome the inhibition of RecA by single-stranded DNA-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):30005-13. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7962001
-
Biochemical interaction of the Escherichia coli RecF, RecO, and RecR proteins with RecA protein and single-stranded DNA binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3875-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3875. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8483906 Free PMC article.
-
The RecOR proteins modulate RecA protein function at 5' ends of single-stranded DNA.EMBO J. 2001 Dec 17;20(24):7313-22. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.24.7313. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11743007 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of bacterial RecA protein function.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Jan-Feb;42(1):41-63. doi: 10.1080/10409230701260258. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17364684 Review.
-
The Role of the RecFOR Complex in Genome Stability.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5441. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125441. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein interactions in genome maintenance as novel antibacterial targets.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058765. Epub 2013 Mar 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23536821 Free PMC article.
-
Single molecule analysis of Thermus thermophilus SSB protein dynamics on single-stranded DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(6):3821-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1316. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24371279 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanism for single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSB) displacement from single-stranded DNA upon SSB-RecO interaction.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):6720-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.164210. Epub 2010 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21169364 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule observation of ATP-independent SSB displacement by RecO in Deinococcus radiodurans.Elife. 2020 Apr 16;9:e50945. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50945. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32297860 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of recF in 254 nm ultraviolet radiation resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans and Escherichia coli.Curr Microbiol. 2010 Nov;61(5):458-64. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9638-x. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Curr Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20386912
References
-
- Krogh BO, Symington LS. Recombination proteins in yeast. Annu Rev. Genet. 2004;38:233–271. - PubMed
-
- Yang H, Li Q, Fan J, Holloman WK, Pavletich NP. The BRCA2 homologue Brh2 nucleates RAD51 filament formation at a dsDNA-ssDNA junction. Nature. 2005;433:653–657. - PubMed
-
- Song B, Sung P. Functional interactions among yeast Rad51 recombinase, Rad52 mediator, and replication protein A in DNA strand exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:15895–15904. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama T, Kowalczykowski SC. Rad52 protein associates with replication protein A (RPA)-single-stranded DNA to accelerate Rad51-mediated displacement of RPA and presynaptic complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:31663–31672. - PubMed

