Ovulatory response to treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is associated with a polymorphism in the STK11 gene
- PMID: 18000088
- PMCID: PMC2266955
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2007-1736
Ovulatory response to treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is associated with a polymorphism in the STK11 gene
Abstract
Context: Clomiphene and insulin sensitizers such as metformin are used to induce ovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), but the ovulatory response is variable, and the causes of this variation are poorly understood.
Objective: Our objective was to identify predictive genetic polymorphisms and other determinants of ovulatory response.
Design: This was a substudy of a multicenter randomized clinical trial.
Setting: This study was performed at academic medical centers and their affiliates.
Participants: A total of 312 women with PCOS were included in the study.
Main outcome measures: Historical, biometric, biochemical, and genetic parameters were performed.
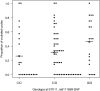
Results: We found that the C allele of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the STK11 gene (expressed in liver; also known as LKB1) was associated with a significantly decreased chance of ovulation in PCOS women treated with metformin. In an analysis of ovulation per cycle, the adjusted odds ratio (OR) comparing the C/C genotype to the G/G genotype was 0.30 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.14, 0.66], and the OR for the C/G genotype vs. the G/G genotype was also 0.30 (95% CI 0.14, 0.66). In an analysis of metformin-treated subjects, we found that the percentage of women who ovulated increased with the number of G alleles present: 48% (10 of 21) of C/C women, 67% (32 of 48) of C/G women, and 79% (15 of 19) of G/G women ovulated. We also found that increased frequency of ovulation was associated with lower body mass index (BMI) [adjusted OR of 2.36 (95% CI 1.65, 3.36) and 2.05 (95% CI 1.46, 2.88), respectively, for comparisons of BMI less than 30 vs. BMI equal to or more than 35, BMI 30-34 vs. BMI equal to or more than 35, in the analysis of ovulation per cycle], a lower free androgen index (FAI) [adjusted OR of 1.59 (95% CI 1.17, 2.18) for FAI<10 vs. FAI>or=10], and a shorter duration of attempting conception [adjusted OR of 1.63 (95% CI 1.20, 2.21) for<1.5 vs.>or=1.5 yr].
Conclusions: We have demonstrated that a polymorphism in STK11, a kinase gene expressed in liver and implicated in metformin action, is associated with ovulatory response to treatment with metformin alone in a prospective randomized trial. The interaction with the effects of changes in modifiable factors (e.g. BMI or FAI) requires further study.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00068861.
Figures
References
-
- Richards JS 2007 Genetics of ovulation. Semin Reprod Med 25:235–242 - PubMed
-
- Azziz R, Woods KS, Reyna R, Key TJ, Knochenhauer ES, Yildiz BO 2004 The prevalence and features of the polycystic ovary syndrome in an unselected population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2745–2749 - PubMed
-
- Broekmans FJ, Knauff EA, Valkenburg O, Laven JS, Eijkemans MJ, Fauser BC 2006 PCOS according to the Rotterdam consensus criteria: change in prevalence among WHO-II anovulation and association with metabolic factors. BJOG 113:1210–1217 - PubMed
-
- Legro RS, Myers E 2004 Surrogate end-points or primary outcomes in clinical trials in women with polycystic ovary syndrome? Hum Reprod 19:1697–1704 - PubMed
-
- Johnson NP 2006 No more surrogate end-points in randomised trials: the PCOSMIC trial protocol for women with polycystic ovary syndrome using metformin for infertility with clomiphene. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 46:141–145 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HD038988/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD039005/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR010732/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27049/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR016499/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD034449/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54-HD29834/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD038999/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD033172/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD029834/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027049/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27011/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027011/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD38997/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR10732/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD34449/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD33172/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD38998/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD038998/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD39005/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD038992/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD38992/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD38999/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD038997/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD38988/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States

