Epigenetic alteration of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 promoter occurs early in the carcinogenesis of Barrett's esophagus
- PMID: 18005197
- PMCID: PMC11158554
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00663.x
Epigenetic alteration of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 promoter occurs early in the carcinogenesis of Barrett's esophagus
Abstract
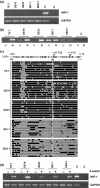
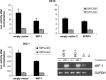
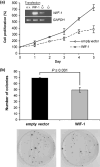
The role of Wnt antagonists in the carcinogenesis of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) remains unclear. We hypothesized that downregulation of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 (WIF-1) might be involved in the neoplastic progression of Barrett's esophagus (BE). We analyzed the DNA methylation status of the WIF-1 promoter in normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic samples from BE patients and in EAC cell lines. We investigated the role of WIF-1 on EAC cell growth and the chemosensitization of the cells to cisplatin. We found that silencing of WIF-1 correlated with promoter hypermethylation. EAC tissue samples showed higher levels of WIF-1 methylation compared to the matched normal epithelium. In addition, we found that WIF-1 hypermethylation was more frequent in BE samples from patients with EAC than in BE samples from patients who had not progressed to EAC. Restoration of WIF-1 in cell lines where WIF-1 was methylation-silenced resulted in growth suppression. Restoration of WIF-1 could sensitize the EAC cells to the chemotherapy drug cisplatin. Our results suggest that silencing of WIF-1 through promoter hypermethylation is an early and common event in the carcinogenesis of BE. Restoring functional WIF-1 might be used as a new targeted therapy for the treatment of this malignancy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypermethylation of the AKAP12 promoter is a biomarker of Barrett's-associated esophageal neoplastic progression.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008 Jan;17(1):111-7. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0407. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008. PMID: 18199717
-
Alterations of the Wnt signaling pathway during the neoplastic progression of Barrett's esophagus.Oncogene. 2006 May 18;25(21):3084-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209338. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16407829
-
Subtypes of Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma based on genome-wide methylation analysis.Gut. 2019 Mar;68(3):389-399. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314544. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Gut. 2019. PMID: 29884612 Free PMC article.
-
Role of epigenetic alterations in the pathogenesis of Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(5):382-96. Epub 2012 May 23. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22808291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Evolution of Metaplasia to Adenocarcinoma in the Esophagus.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Aug;63(8):2059-2069. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5090-8. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29766388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Drosophila WIF1 homolog Shifted maintains glypican-independent Hedgehog signaling and interacts with the Hedgehog co-receptors Ihog and Boi.Development. 2013 Jan 1;140(1):107-16. doi: 10.1242/dev.078444. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Development. 2013. PMID: 23154411 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt inhibitory factor 1 decreases tumorigenesis and metastasis in osteosarcoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Mar;9(3):731-41. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0147. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20197388 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Activation beyond Robust Nuclear β-Catenin Accumulation in Nondysplastic Barrett's Esophagus: Regulation via Dickkopf-1.Neoplasia. 2015 Jul;17(7):598-611. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2015.07.006. Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26297437 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma.HPB (Oxford). 2011 Jun;13(6):369-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2011.00303.x. Epub 2011 Mar 29. HPB (Oxford). 2011. PMID: 21609368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-Analysis Based on Nonconvex Regularization.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 1;10(1):5755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62473-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32238826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK. The changing epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Semin Oncol 1999; 26: 2–8. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004; 20: 781–810. - PubMed
-
- Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1837–51. - PubMed
-
- Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V et al . Activation of beta‐catenin‐Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta‐catenin or APC. Science 1997; 275: 1787–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

