Epigenetic alteration of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 promoter occurs early in the carcinogenesis of Barrett's esophagus
- PMID: 18005197
- PMCID: PMC11158554
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00663.x
Epigenetic alteration of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 promoter occurs early in the carcinogenesis of Barrett's esophagus
Abstract
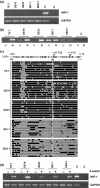
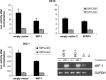
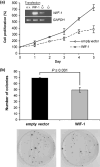
The role of Wnt antagonists in the carcinogenesis of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) remains unclear. We hypothesized that downregulation of the Wnt inhibitory factor-1 (WIF-1) might be involved in the neoplastic progression of Barrett's esophagus (BE). We analyzed the DNA methylation status of the WIF-1 promoter in normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic samples from BE patients and in EAC cell lines. We investigated the role of WIF-1 on EAC cell growth and the chemosensitization of the cells to cisplatin. We found that silencing of WIF-1 correlated with promoter hypermethylation. EAC tissue samples showed higher levels of WIF-1 methylation compared to the matched normal epithelium. In addition, we found that WIF-1 hypermethylation was more frequent in BE samples from patients with EAC than in BE samples from patients who had not progressed to EAC. Restoration of WIF-1 in cell lines where WIF-1 was methylation-silenced resulted in growth suppression. Restoration of WIF-1 could sensitize the EAC cells to the chemotherapy drug cisplatin. Our results suggest that silencing of WIF-1 through promoter hypermethylation is an early and common event in the carcinogenesis of BE. Restoring functional WIF-1 might be used as a new targeted therapy for the treatment of this malignancy.
Figures



References
-
- Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK. The changing epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Semin Oncol 1999; 26: 2–8. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004; 20: 781–810. - PubMed
-
- Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1837–51. - PubMed
-
- Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V et al . Activation of beta‐catenin‐Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta‐catenin or APC. Science 1997; 275: 1787–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

