Increased weight loss with reduced viral replication in interleukin-10 knock-out mice infected with murine cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 18005264
- PMCID: PMC2276919
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03533.x
Increased weight loss with reduced viral replication in interleukin-10 knock-out mice infected with murine cytomegalovirus
Abstract
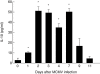
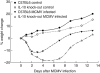
The anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-10 plays an important role in the regulation of host-immune responses. Here we studied the role IL-10 plays in host responses to cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. We demonstrate that manifestations of murine CMV (MCMV) disease are more severe in IL-10 knock-out mice, despite significantly reduced levels of viral replication. Cytokine analysis of serum revealed increased levels of interferon (IFN)-gamma, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) and IL-6, all of which are potent stimulators of inflammatory responses. Depletion of IFN-gamma by monoclonal antibodies in IL-10 knock-out mice failed to improve the physical condition of the mice, while increasing viral replication. In contrast, serum levels of IL-6 in the knock-out animals were unaffected by IFN-gamma depletion and remained significantly elevated early in the course of infection. These data suggest that increased weight loss observed in IL-10 knock-out mice may be attributed to the uncontrolled production of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6.
Figures


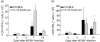

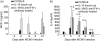
References
-
- Nordoy I, Muller F, Nordal KP, et al. The role of the tumor necrosis factor system and interleukin-10 during cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:51–7. - PubMed
-
- Opal SM, Wherry JC, Grint P. Interleukin-10: potential benefits and possible risks in clinical infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:1497–507. - PubMed
-
- Chang HR, Bistrian B. The role of cytokines in the catabolic consequences of infection and injury. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1998;22:156–66. - PubMed
-
- Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O'Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

