Peptide ligand screening of alpha-synuclein aggregation modulators by in silico panning
- PMID: 18005454
- PMCID: PMC2244645
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-451
Peptide ligand screening of alpha-synuclein aggregation modulators by in silico panning
Abstract
Background: alpha-Synuclein is a Parkinson's-disease-related protein. It forms aggregates in vivo, and these aggregates cause cell cytotoxicity. Aggregation inhibitors are expected to reduce alpha-synuclein cytotoxicity, and an aggregation accelerator has recently been reported to reduce alpha-synuclein cytotoxicity. Therefore, amyloid aggregation modulating ligands are expected to serve as therapeutic medicines.
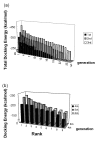
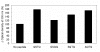
Results: We screened peptide ligands against alpha-synuclein by in silico panning, a method which we have proposed previously. In this study, we selected as the target a very hydrophobic region known as the amyloid-core-forming region. Since this region cannot be dissolved in water, it is difficult to carry out the in vitro screening of its peptide ligand. We carried out 6 rounds of in silico panning using a genetic algorithm and a docking simulation. After the in silico panning, we evaluated the top peptides screened in silico by in vitro assay. These peptides were capable of binding to alpha-synuclein.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that it is possible to screen alpha-synuclein-binding peptides by in silico panning. The screened peptides bind to alpha-synuclein, thus affecting the aggregation of alpha-synuclein.
Figures
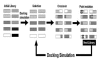

References
-
- Conway KA, Lee SJ, Rochet JC, Ding TT, Williamson RE, Lansbury PT., Jr. Acceleration of oligomerization, not fibrillization, is a shared property of both alpha-synuclein mutations linked to early-onset Parkinson's disease: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:571–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.571. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

