Seasonality of clinical isolation of rapidly growing mycobacteria
- PMID: 18005476
- PMCID: PMC2870912
- DOI: 10.1017/S095026880700982X
Seasonality of clinical isolation of rapidly growing mycobacteria
Abstract
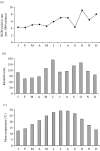
Rapidly growing mycobacteria (RGM) are environmental organisms that have emerged as significant human pathogens. RGM infections show remarkable geographic variations. In this study, based on data from Houston, Texas, RGM were isolated from clinical cultures year-round, although peaks in the summer and autumn correlating with the seasonal variation of temperature and rainfall also were noted. These results may offer some explanation for the summer occurrence of RGM outbreaks at diverse locations.
Figures
References
-
- Bolan G et al. Infections with Mycobacterium chelonei in patients receiving dialysis and using processed hemodialyzers. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1985;152:1013–1019. - PubMed
-
- Kline S et al. An outbreak of bacteremias associated with Mycobacterium mucogenicum in a hospital water supply. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 2004;25:1042–1049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical