A plasmid-based reverse genetics system for animal double-stranded RNA viruses
- PMID: 18005692
- PMCID: PMC2034303
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.03.003
A plasmid-based reverse genetics system for animal double-stranded RNA viruses
Erratum in
- Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Aug 16;2(2):139
Abstract
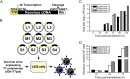
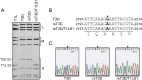
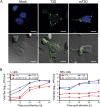
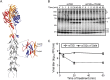
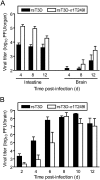
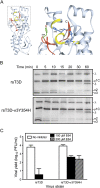
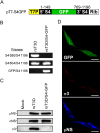
Mammalian orthoreoviruses (reoviruses) are highly tractable experimental models for studies of double-stranded (ds) RNA virus replication and pathogenesis. Reoviruses infect respiratory and intestinal epithelium and disseminate systemically in newborn animals. Until now, a strategy to rescue infectious virus from cloned cDNA has not been available for any member of the Reoviridae family of dsRNA viruses. We report the generation of viable reovirus following plasmid transfection of murine L929 (L) cells using a strategy free of helper virus and independent of selection. We used the reovirus reverse genetics system to introduce mutations into viral capsid proteins sigma1 and sigma3 and to rescue a virus that expresses a green fluorescent protein (GFP) transgene, thus demonstrating the tractability of this technology. The plasmid-based reverse genetics approach described here can be exploited for studies of reovirus replication and pathogenesis and used to develop reovirus as a vaccine vector.
Figures
Comment in
-
A Reverse genetics system for dsRNA viruses.Cell Host Microbe. 2007 Apr 19;1(2):90-1. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.04.004. Cell Host Microbe. 2007. PMID: 18005686
References
-
- Barton E.S., Connolly J.L., Forrest J.C., Chappell J.D., Dermody T.S. Utilization of sialic acid as a coreceptor enhances reovirus attachment by multistep adhesion strengthening. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:2200–2211. - PubMed
-
- Barton E.S., Forrest J.C., Connolly J.L., Chappell J.D., Liu Y., Schnell F., Nusrat A., Parkos C.A., Dermody T.S. Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus. Cell. 2001;104:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Blaney J.E., Jr., Durbin A.P., Murphy B.R., Whitehead S.S. Development of a live attenuated dengue virus vaccine using reverse genetics. Viral Immunol. 2006;19:10–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM08554/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI62862/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032539/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI07611/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI71440/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI07281/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI038296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI038296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007611/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI38296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM07347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI49824/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI049824/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI32539/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007281/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008554/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI071440/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI062862/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA09385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

