Inhibition of Raf-1 alters multiple downstream pathways to induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis
- PMID: 18006502
- PMCID: PMC3025401
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M703612200
Inhibition of Raf-1 alters multiple downstream pathways to induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis
Abstract
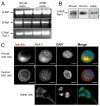
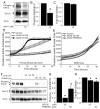
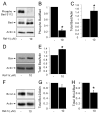
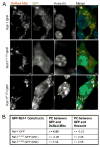
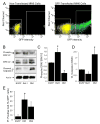
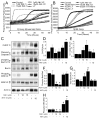
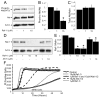
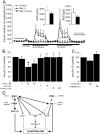
The serine threonine kinase Raf-1 plays a protective role in many cell types, but its function in pancreatic beta-cells has not been elucidated. In the present study, we examined whether primary beta-cells possess Raf-1 and tested the hypothesis that Raf-1 is critical for beta-cell survival. Using reverse transcriptase-PCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence, we identified Raf-1 in human islets, mouse islets, and in the MIN6 beta-cell line. Blocking Raf-1 activity using a specific Raf-1 inhibitor or dominant-negative Raf-1 mutants led to a time- and dose-dependent increase in cell death, assessed by real-time imaging of propidium iodide incorporation, TUNEL, PCR-enhanced DNA laddering, and Caspase-3 cleavage. Although the rapid increase in apoptotic cell death was associated with decreased Erk phosphorylation, studies with two Mek inhibitors suggested that the classical Erk-dependent pathway could explain only part of the cell death observed after inhibition of Raf-1. An alternative Erk-independent pathway downstream of Raf-1 kinase involving the pro-apoptotic protein Bad has recently been characterized in other tissues. Inhibiting Raf-1 in beta-cells led to a striking loss of Bad phosphorylation at serine 112 and an increase in the protein levels of both Bad and Bax. Together, our data strongly suggest that Raf-1 signaling plays an important role regulating beta-cell survival, via both Erk-dependent and Bad-dependent mechanisms. Conversely, acutely inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Akt had more modest effects on beta-cell death. These studies identify Raf-1 as a critical anti-apoptotic kinase in pancreatic beta-cells and contribute to our understanding of survival signaling in this cell type.
Figures

References
-
- Donath MY, Halban P. Diabetologia. 2004;47:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran S, Desai NM, Goers TA, Benshoff N, Olack B, Shenoy S, Jendrisak MD, Chapman WC, Mohanakumar T. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:1696–1703. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni RN, Bruning JC, Winnay JN, Postic C, Magnuson MA, Kahn CR. Cell. 1999;96:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto N, Kido Y, Uchida T, Asahara S, Shigeyama Y, Matsuda T, Takeda A, Tsuchihashi D, Nishizawa A, Ogawa W, Fujimoto Y, Okamura H, Arden KC, Herrera PL, Noda T, Kasuga M. Nat Genet. 2006;38:589–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

