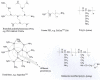
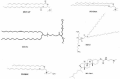
Polymers for DNA delivery
- PMID: 18007276
- PMCID: PMC6147627
- DOI: 10.3390/10010034
Polymers for DNA delivery
Abstract
Nucleic acid delivery has many applications in basic science, biotechnology, agriculture, and medicine. One of the main applications is DNA or RNA delivery for gene therapy purposes. Gene therapy, an approach for treatment or prevention of diseases associated with defective gene expression, involves the insertion of a therapeutic gene into cells, followed by expression and production of the required proteins. This approach enables replacement of damaged genes or expression inhibition of undesired genes. Following two decades of research, there are two major methods for delivery of genes. The first method, considered the dominant approach, utilizes viral vectors and is generally an efficient tool of transfection. Attempts, however, to resolve drawbacks related with viral vectors (e.g., high risk of mutagenicity, immunogenicity, low production yield, limited gene size, etc.), led to the development of an alternative method, which makes use of non-viral vectors. This review describes non-viral gene delivery vectors, termed "self-assembled" systems, and are based on cationic molecules, which form spontaneous complexes with negatively charged nucleic acids. It introduces the most important cationic polymers used for gene delivery. A transition from in vitro to in vivo gene delivery is also presented, with an emphasis on the obstacles to achieve successful transfection in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cationic polymer optimization for efficient gene delivery.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2010 Feb;10(2):108-25. doi: 10.2174/138955710791185109. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20408796 Review.
-
Impact of DNA vector topology on non-viral gene therapeutic safety and efficacy.Curr Gene Ther. 2014;14(4):309-29. doi: 10.2174/1566523214666140612154929. Curr Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25039613 Review.
-
Current status of non-viral gene therapy for CNS disorders.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016 Oct;13(10):1433-45. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1188802. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27249310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Lipopolyplexes for Gene Transfection: Comparing 2D, 3D and Microdroplet-Enabled Cell Culture.Molecules. 2020 Jul 18;25(14):3277. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143277. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32708478 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired Star-Shaped Poly(l-lysine) Polypeptides: Efficient Polymeric Nanocarriers for the Delivery of DNA to Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Mol Pharm. 2018 May 7;15(5):1878-1891. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00044. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29590755
Cited by
-
Recent Findings Concerning PAMAM Dendrimer Conjugates with Cyclodextrins as Carriers of DNA and RNA.Sensors (Basel). 2009;9(8):6346-61. doi: 10.3390/s90806346. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Sensors (Basel). 2009. PMID: 22454589 Free PMC article.
-
Multilayered Nanoparticles for Gene Delivery Used to Reprogram Human Foreskin Fibroblasts to Neurospheres.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015 Aug;21(8):786-94. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2014.0482. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015. PMID: 25687130 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 17;12:786255. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.786255. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35111077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of EGFR monoclonal antibody conjugated nanoparticles and targeting to hepatocellular carcinoma.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010 Feb;21(2):551-6. doi: 10.1007/s10856-009-3925-8. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010. PMID: 19921404
-
Optimizing Nanoparticle Design for Gene Therapy: Protection of Oligonucleotides from Degradation Without Impeding Release of Cargo.Nanomed Nanosci Res. 2018;2(6):155. doi: 10.29011/2577-1477.100055. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Nanomed Nanosci Res. 2018. PMID: 31058264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hullett D. A. Gene therapy in transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 1996;15:857–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources