Covalent polymer-drug conjugates
- PMID: 18007281
- PMCID: PMC6147706
- DOI: 10.3390/10010114
Covalent polymer-drug conjugates
Abstract
In this work, polymer-drugs conjugates used as drug delivery systems (DDS) are revised attending to their chemical conjugation. Namely, the classification of this type of DDS is based on the conjugation sites of the reactive groups (i.e., via end groups or pendant polymer groups). Advantages and limitations of these types of DDS are discussed through representative examples of polymer-drugs and polymer-proteins conjugates recently developed.
Figures


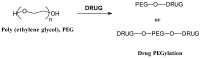


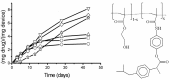
 ), 20 (
), 20 ( ) and 30 % (
) and 30 % ( ).
).References
-
- Mathiowitz E. Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery. Wiley-Interscience; New York: 1999.
-
- Kydonieus A. Treatise on Controlled Drug Delivery. Marcel Dekker; New York: 1992.
-
- Baker R. Controlled Release of Biologically Active Agents. Academic Press; New York: 1987.
-
- Shiino D., Murata Y., Kataoka K., Koyama Y., Yokoyama M., Okano T., Sakurai Y. Preparation and characterization of a glucose-responsive insulin-releasing polymer device. Biomaterials. 1994;15:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg L.E., Ron E.S. Temperature-responsive gels and thermogelling polymer matrices for protein and peptide delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998;31:197–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

