Probing the structure of DNA aptamers with a classic heterocycle
- PMID: 18007412
- PMCID: PMC6147400
- DOI: 10.3390/90300067
Probing the structure of DNA aptamers with a classic heterocycle
Abstract
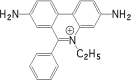
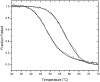
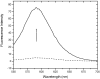
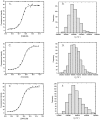
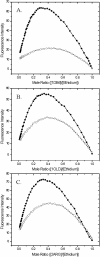
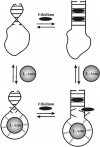
DNA aptamers are synthetic, single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides selected by SELEX methods for their binding with specific ligands. Here we present ethidium binding results for three related DNA aptamers (PDB code: 1OLD, 1DB6, and 2ARG)that bind L-argininamide (L-Arm). The ligand bound form of each aptamer's structure has been reported and each are found to be composed primarily of two domains consisting of a stem helical region and a loop domain that forms a binding pocket for the cognate ligand. Previous thermodynamic experiments demonstrated that the DNA aptamer 1OLD undergoes a large conformational ordering upon binding to L-Arm. Here we extend those linkage binding studies by examining the binding of the heterocyclic intercalator ethidium to each of the three aptamers by fluorescence and absorption spectrophotometric titrations. Our results reveal that ethidium binds to each aptamer with DeltaG degree's in the range of -8.7 to -9.4 kcal/mol. The stoichiometry of binding is 2:1 for each aptamer and is quantitatively diminished in the presence of L-Arm as is the overall fluorescence intensity of ethidium. Together, these results demonstrate that a portion of the bound ethidium is excluded from the aptamer in the presence of a saturating amount of L-Arm. These results demonstrate the utility of ethidium and related compounds for the probing of non-conventional DNA structures and reveal an interesting fundamental thermodynamic linkage in DNA aptamers. Results are discussed in the context of the thermodynamic stability and structure of each of the aptamers examined.
Figures
References
-
- Tinoco I., Jr. From RNA hairpins to kisses to pseudoknots. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1997;36:49. - PubMed
-
- Darlow J.M., Leach D.R. Evidence for two preferred hairpin folding patterns in d(CGG).d(CCG) repeat tracts in vivo. J. Mol. Biol. 1998;275:17. - PubMed
-
- Moody E.M., Bevilacqua P.C. Folding of a stable DNA motif involves a highly cooperative network of interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:16285. - PubMed
-
- Armitage B.A. The impact of nucleic acid secondary structure on PNA hybridization. Drug Discov Today. 2003;8:222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

