Genetic loci affecting body weight and fatness in a C57BL/6J x PWK/PhJ mouse intercross
- PMID: 18008102
- PMCID: PMC2131744
- DOI: 10.1007/s00335-007-9069-6
Genetic loci affecting body weight and fatness in a C57BL/6J x PWK/PhJ mouse intercross
Abstract
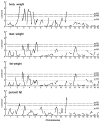
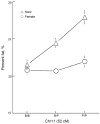
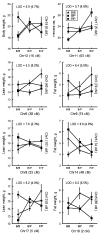
To determine the genetic variation that contributes to body composition in the mouse, we interbred a wild-derived strain (PWK/PhJ; PWK) with a common laboratory strain (C57BL/6J; B6). The parental, F(1), and F(2) mice were phenotyped at 18 weeks old for body weight and composition using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). A total of 479 (244 male and 235 female) F(2) mice were genotyped for 117 polymorphic markers spanning the autosomes. Twenty-eight suggestive or significant linkages for four traits (body weight, adjusted lean and fat weight, and percent fat) were detected. Of these, three QTLs were novel: one on the proximal portion of Chr 5 for body weight (Bwq8; LOD = 4.7), one on Chr 3 for lean weight (Bwtq13; LOD = 3.6), and one on Chr 11 for percent fat (Adip19; LOD = 5.8). The remaining QTLs overlapped previously identified linkages, e.g., Adip5 on Chr 9. One QTL was sex-specific (present in males only) and seven were sex-biased (more prominent in one sex than the other). Most alleles that increased body weight were contributed by the B6 strain, and most alleles that increased percent fat were contributed by the PWK strain. Eight pairs of interacting loci were identified, none of which exactly overlapped the main-effect QTLs. Many of the QTLs found in the B6 x PWK cross map to the location of previously reported linkages, suggesting that some QTLs are common to many strains (consensus QTLs), but three new QTLs appear to be particular to the PWK strain. The location and type of QTLs detected in this new cross will assist in future efforts to identify the genetic variation that determines the ratio of lean to fat weight as well as body size in mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic and genomic analysis of hyperlipidemia, obesity and diabetes using (C57BL/6J × TALLYHO/JngJ) F2 mice.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 19;11:713. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-713. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21167066 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-influenced obesity QTLs identified in a cross involving the KK type II diabetes-prone mouse strain.Mamm Genome. 1999 Oct;10(10):963-8. doi: 10.1007/s003359901141. Mamm Genome. 1999. PMID: 10501964
-
Loci on chromosomes 2, 4, 9, and 16 for body weight, body length, and adiposity identified in a genome scan of an F2 intercross between the 129P3/J and C57BL/6ByJ mouse strains.Mamm Genome. 2003 May;14(5):302-13. doi: 10.1007/s00335-002-2170-y. Mamm Genome. 2003. PMID: 12856282 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple obesity QTLs identified in an intercross between the NZO (New Zealand obese) and the SM (small) mouse strains.Mamm Genome. 2001 Feb;12(2):95-103. doi: 10.1007/s003350010254. Mamm Genome. 2001. PMID: 11210195
-
Gene discovery and the genetic basis of calcium consumption.Physiol Behav. 2008 Aug 6;94(5):649-59. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 Apr 13. Physiol Behav. 2008. PMID: 18499198 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATR-FTIR spectroscopy reveals genomic loci regulating the tissue response in high fat diet fed BXD recombinant inbred mouse strains.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jun 10;14:386. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-386. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23758785 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Nob3, a major quantitative trait locus for obesity and hyperglycemia on mouse chromosome 1.Physiol Genomics. 2009 Jul 9;38(2):226-32. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00011.2009. Epub 2009 May 26. Physiol Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19470805 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Rapid and Extreme Size Evolution in Island Mice.Genetics. 2015 Sep;201(1):213-28. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.177790. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26199233 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Autophagy on Chronic Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia Ameliorating Liver Damage in Metabolic Syndrome Rats.Front Physiol. 2020 Jan 30;11:13. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00013. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32082187 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of T1R3 in calcium-magnesium taste.Physiol Genomics. 2008 Aug 15;34(3):338-48. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.90200.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Physiol Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18593862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anunciado RV, Nishimura M, Mori M, Ishikawa A, Tanaka S, et al. Quantitative trait loci for body weight in the intercross between SM/J and A/J mice. Exp Anim. 2001;50:319–324. - PubMed
-
- Bennett B, Carosone-Link PJ, Lu L, Chesler EJ, Johnson TE. Genetics of body weight in the LXS recombinant inbred mouse strains. Mamm Genome. 2005;16:764–774. - PubMed
-
- Bogue MA, Grubb SC. The Mouse Phenome Project. Genetica. 2004;122:71–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

