Importance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives
- PMID: 18019829
- PMCID: PMC2676658
Importance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives
Abstract
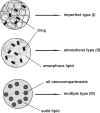
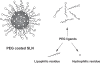
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) have been reported to be an alternative system to emulsions, liposomes, microparticles and their polymeric counterparts for various application routes since the early 1990s due to their advantages. Various research groups have also increasingly focused on improving their stability in body fluids after administration by coating of particles with hydrophilic molecules such as poly(ethylene)glycol (PEG) derivatives. Altering surface characteristics by coating SLN with hydrophilic molecules improves plasma stability and biodistribution, and subsequent bioavailability of drugs entrapped. Their storage stability is also increased. This paper basicly reviews types of SLN, principles of drug loading and models of drug incorporation. The influence of PEG coating on particle size and surface characteristics is discussed followed by alteration in pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of drugs in order to target the site of action via SLN. The future direction of research and clinical implications of SLN is also considered.
Figures

References
-
- Abuchowski A, Van Es T, Palczuk NC, et al. Alteration of immunological properties of bovine serum albumin by covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol. J Biol Chem. 1977;252:3578–81. - PubMed
-
- Abuchowski A, Kazo GM, Verhoest CR, et al. Cancer therapy with chemically modified enzymes. I. Antitumor properties of poly-ethylene glycol asparaginase conjugates. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 1984;7:175–86. - PubMed
-
- Acar HY, Garaas RS, Syud F, et al. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles stabilized by polimerized PEGylated coatings. J Magnet Magnet Mater. 2005;293:1–7.
-
- Banga AK. Deivery of protein therapeutics. Business Briefing: Pharmatech. 2003:198–201.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
