Impaired photoreceptor protein transport and synaptic transmission in a mouse model of Bardet-Biedl syndrome
- PMID: 18022666
- PMCID: PMC2661240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2007.09.016
Impaired photoreceptor protein transport and synaptic transmission in a mouse model of Bardet-Biedl syndrome
Abstract
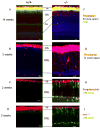
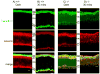
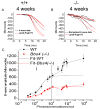
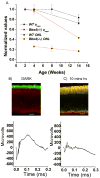
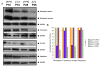
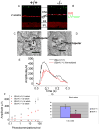
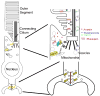
Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) is an oligogenic syndrome whose manifestations include retinal degeneration, renal abnormalities, obesity and polydactylia. Evidence suggests that the main etiopathophysiology of this syndrome is impaired intraflagellar transport (IFT). In this study, we study the Bbs4-null mouse and investigate photoreceptor structure and function after loss of this gene. We find that Bbs4-null mice have defects in the transport of phototransduction proteins from the inner segments to the outer segments, before signs of cell death. Additionally, we show defects in synaptic transmission from the photoreceptors to secondary neurons of the visual system, demonstrating multiple functions for BBS4 in photoreceptors.
Figures


References
-
- Ansley SJ, Badano JL, Blacque OE, Hill J, Hoskins BE, Leitch CC, Kim JC, Ross AJ, Eichers ER, Teslovich TM, Mah AK, Johnsen RC, Cavender JC, Lewis RA, Leroux MR, Beales PL, Katsanis N. Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature. 2003;425(6958):628–33. 9. - PubMed
-
- Bascom RA, Manara S, Collins L, Molday RS, Kalnins VI, McInnes RR. Cloning of the cDNA for a novel photoreceptor membrane protein (rom-1) identifies a disk rim protein family implicated in human retinopathies. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1171–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

